Surface activity of surfactant spiked with vitamin A
- PMID: 19920902
- PMCID: PMC2761185
- DOI: 10.2147/dddt.s3255
Surface activity of surfactant spiked with vitamin A
Abstract
Background: Intramuscular injections of vitamin A decrease the risk of broncho-pulmonary dysplasia. Admixture of vitamin A with surfactant as a lipophilic vehicle might be a less invasive modality.
Aim: Test physical properties of surfactant + vitamin A.
Methods: Miscibility and surface activity were tested in surfactant supplemented with retinyl-acetate, -palmitate, 13-cis-, or all-trans-retinoic acid.
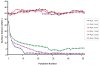
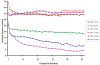
Results: Retinol acetate (5000 IU/mL) demonstrated miscibility with surfactant when premixing with ethanol. Its surface activity was 40% lower compared to surfactant alone.
Conclusion: These findings warrant preclinical studies to test whether administration of vitamin A in subjects requiring surfactant is associated with beneficial functional properties.
Keywords: drug delivery; surface tension; surfactant; vitamin A.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Repeated topical treatment, in contrast to single oral doses, with Vitamin A-containing preparations does not affect plasma concentrations of retinol, retinyl esters or retinoic acids in female subjects of child-bearing age.Toxicol Lett. 2006 May 5;163(1):65-76. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2005.09.029. Epub 2005 Oct 21. Toxicol Lett. 2006. PMID: 16243460 Clinical Trial.
-
Serum retinoids in retinitis pigmentosa patients treated with vitamin A.Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 1996 Aug;234 Suppl 1:S18-21. doi: 10.1007/BF02343043. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 1996. PMID: 8871145
-
Retinoids control surfactant phospholipid biosynthesis in fetal rat lung.Am J Physiol. 1994 Jun;266(6 Pt 1):L705-12. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1994.266.6.L705. Am J Physiol. 1994. PMID: 8023960
-
Unoccluded retinol penetrates human skin in vivo more effectively than unoccluded retinyl palmitate or retinoic acid.J Invest Dermatol. 1997 Sep;109(3):301-5. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12335788. J Invest Dermatol. 1997. PMID: 9284094
-
Comparative teratology and transplacental pharmacokinetics of all-trans-retinoic acid, 13-cis-retinoic acid, and retinyl palmitate following daily administrations in rats.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1994 Jul;127(1):132-44. doi: 10.1006/taap.1994.1147. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1994. PMID: 8048045
Cited by
-
Preterm infants: is prophylactic surfactant therapy and early vitamin A supplementation the way ahead?Med J Armed Forces India. 2011 Apr;67(2):102-3. doi: 10.1016/S0377-1237(11)60001-4. Epub 2011 Jul 21. Med J Armed Forces India. 2011. PMID: 27365778 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Biophysical interaction between corticosteroids and natural surfactant preparation: implications for pulmonary drug delivery using surfactant a a carrier.Soft Matter. 2012 Jan 14;8(2):504-511. doi: 10.1039/c1sm06444d. Epub 2011 Nov 1. Soft Matter. 2012. PMID: 28747989 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allwood MC, Martin HJ. The photodegradation of vitamins A and E in parenteral nutrition mixtures during infusion. Clin Nutr. 2000;19:339–42. - PubMed
-
- Ambalavan N, Wu TJ, Tyson JE, et al. A comparison of three vitamin A dosing regimens in extremely-low-birth-weight-infants. J Pediatr. 2003;142:656–61. - PubMed
-
- Ambalavanan N, Kennedy K, Tyson J, et al. Survey of vitamin A supplementation for extremely-low-birth-weight infants: is clinical practice consistent with the evidence? J Pediatr. 2004;145:304–7. - PubMed
-
- Bernhard W, Mottaghian J, Gebert A, et al. Commercial versus native surfactants. Surface activity, molecular components, and the effect of calcium. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000;162:1524–33. - PubMed
-
- Biesalski HK, Reifen R, Furst RP, et al. Retinyl palmitate supplementation by inhalation of an aerosol improves vitamin A status of preschool children in Gondar (Ethiopia) Br J Nutr. 1999;82:179–82. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

