Drug design with Cdc7 kinase: a potential novel cancer therapy target
- PMID: 19920912
- PMCID: PMC2761190
- DOI: 10.2147/dddt.s4303
Drug design with Cdc7 kinase: a potential novel cancer therapy target
Abstract
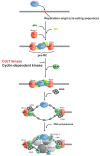
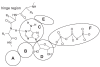
Identification of novel molecular targets is critical in development of new and efficient cancer therapies. Kinases are one of the most common drug targets with a potential for cancer therapy. Cell cycle progression is regulated by a number of kinases, some of which are being developed to treat cancer. Cdc7 is a serine-threonine kinase originally discovered in budding yeast, which has been shown to be necessary to initiate the S phase. Inhibition of Cdc7 in cancer cells retards the progression of the S phase, accumulates DNA damage, and induces p53-independent cell death, but the same treatment in normal cells does not significantly affect of less than viability. Low-molecular-weight compounds that inhibit Cdc7 kinase with an IC(50) 10 nM have been identified, and shown to be effective in the inhibition of tumor growth in animal models. Thus Cdc7 kinase can be recognized as a novel molecular target for cancer therapy.
Keywords: ATP-binding pocket; Cdc7 kinase; DNA damages; cell cycle; genome stability; kinase inhibitor; replication fork.
Figures


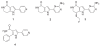

Similar articles
-
Targeting cell division cycle 7 kinase: a new approach for cancer therapy.Clin Cancer Res. 2010 Sep 15;16(18):4503-8. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-0185. Epub 2010 Jul 20. Clin Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20647475 Review.
-
Identification of Novel Cdc7 Kinase Inhibitors as Anti-Cancer Agents that Target the Interaction with Dbf4 by the Fragment Complementation and Drug Repositioning Approach.EBioMedicine. 2018 Oct;36:241-251. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2018.09.030. Epub 2018 Oct 5. EBioMedicine. 2018. PMID: 30293817 Free PMC article.
-
CDC7 kinase inhibitors: a survey of recent patent literature (2017-2022).Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2023 Jul-Dec;33(7-8):493-501. doi: 10.1080/13543776.2023.2262138. Epub 2023 Nov 6. Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2023. PMID: 37735909 Review.
-
Cdc7 inhibition reveals a p53-dependent replication checkpoint that is defective in cancer cells.Cancer Res. 2004 Oct 1;64(19):7110-6. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-1547. Cancer Res. 2004. PMID: 15466207
-
Genetic dissection of mammalian Cdc7 kinase: cell cycle and developmental roles.Cell Cycle. 2004 Mar;3(3):300-4. Epub 2004 Mar 1. Cell Cycle. 2004. PMID: 14726652
Cited by
-
Cdc7 activates replication checkpoint by phosphorylating the Chk1-binding domain of Claspin in human cells.Elife. 2019 Dec 31;8:e50796. doi: 10.7554/eLife.50796. Elife. 2019. PMID: 31889509 Free PMC article.
-
CDC7 as a novel biomarker and druggable target in cancer.Clin Transl Oncol. 2022 Oct;24(10):1856-1864. doi: 10.1007/s12094-022-02853-4. Epub 2022 Jun 3. Clin Transl Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35657477 Review.
-
Co-targeting of specific epigenetic regulators in combination with CDC7 potently inhibit melanoma growth.iScience. 2022 Jul 15;25(8):104752. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.104752. eCollection 2022 Aug 19. iScience. 2022. PMID: 35942091 Free PMC article.
-
PIWI-interacting RNA 021285 is involved in breast tumorigenesis possibly by remodeling the cancer epigenome.Carcinogenesis. 2015 Oct;36(10):1094-102. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgv105. Epub 2015 Jul 25. Carcinogenesis. 2015. PMID: 26210741 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanism of activation of human Cdc7 kinase: bipartite interaction with Dbf4/activator of S phase kinase (ASK) activation subunit stimulates ATP binding and substrate recognition.J Biol Chem. 2011 Jul 1;286(26):23031-43. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.243311. Epub 2011 May 2. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21536671 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bartek J, Lukas J. Chk1 and Chk2 kinases in checkpoint control and cancer. Cancer Cell. 2003;3:421–9. - PubMed
-
- Cherry M, Williams DH. Recent kinase and kinase inhibitor X-ray structures: mechanisms of inhibition and selectivity insights. Curr Med Chem. 2004;11:663–73. - PubMed
-
- Collins I, Garrett MD. Targeting the cell division cycle in cancer: CDK and cell cycle checkpoint kinase inhibitors. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2005;5:366–73. - PubMed
-
- Collins I, Workman P. New approaches to molecular cancer therapeutics. Nat Chem Biol. 2006;2:689–700. - PubMed
-
- Costanzo V, Shechter D, Lupardus PJ, et al. An ATR- and Cdc7-dependent DNA damage checkpoint that inhibits initiation of DNA replication. Mol Cell. 2003;11:203–13. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

