Differential expression of miRNA patterns in renal cell carcinoma and nontumorous tissues
- PMID: 19921256
- PMCID: PMC11827771
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-009-0726-x
Differential expression of miRNA patterns in renal cell carcinoma and nontumorous tissues
Abstract
Introduction: MiRNAs are short single stranded RNAs that are associated with gene regulation at the transcriptional and translational level. Changes in their expression were found in a variety of human cancers. In the present study, we aimed to investigate expression profiles of miRNA (miRNA) in the clear cell subtype of kidney cancer and to develop further understanding of the molecular mechanisms involved in the pathogenesis of renal cell carcinoma.
Materials and methods: We analyzed the miRNA expression profiles in 30 pairs of renal cell carcinoma and adjacent nontumorous tissue (NT), using a mammalian miRNA microarray containing whole human mature and precursor miRNA sequences. Real-time quantitative PCR was performed to confirm the array results.
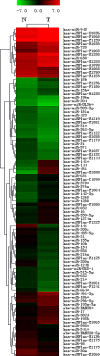
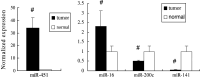
Results: The miRNA microarray chip analysis identified 86 miRNAs differentially expressed in renal cell carcinoma tissues and a total of 38 miRNAs exhibited higher expression in the renal cell carcinoma samples than that in the NT samples, while 48 miRNA demonstrated lower expression in the renal cell carcinoma samples than that in the NT samples.
Conclusion: Quantitative real-time PCR analysis confirmed microarray data. The report supports that many miRNA expressions were altered in renal carcinoma, whose expression profiling may provide a useful clue for the pathophysiology research. However, further longer-term researches are required to investigate the relationship between miRNA and renal carcinoma as well as their role in carcinogenesis.
Figures
References
-
- Bandres E, Bitarte N, Arias F, Agorreta J, Fortes P, Agirre X, Zarate R, Diaz-Gonzalez JA, Ramirez N, Sola JJ, Jimenez P, Rodriguez J, Garcia-Foncillas J (2009) miRNA-451 regulates macrophage migration inhibitory factor production and proliferation of gastrointestinal cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res 15(7):2281–2290 - PubMed
-
- Bartel DP (2004) MiRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116(2):281–297 - PubMed
-
- Chiosea S, Jelezcova E, Chandran U, Luo J, Mantha G, Sobol RW, Dacic S (2007) Overexpression of Dicer in precursor lesions of lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res 67(5):2345–2350 - PubMed
-
- Dai Y, Huang YS, Tang M, Lv TY, Hu CX, Tan YH, Xu ZM, Yin YB (2007) Microarray analysis of microRNA expression in peripheral blood cells of systemic lupus erythematosus patients. Lupus 16(12):939–946 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

