Genotype-phenotype correlation in four 15q24 deleted patients identified by array-CGH
- PMID: 19921647
- PMCID: PMC2874573
- DOI: 10.1002/ajmg.a.33097
Genotype-phenotype correlation in four 15q24 deleted patients identified by array-CGH
Abstract
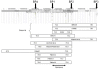
Microdeletion 15q24 is an emerging syndrome recently described, mainly due to increased use of array-CGH. Clinical features associate mild to moderate developmental delay, typical facial characteristics (high forehead and frontal hairline, broad eyebrows, downslanting palpebral features, long philtrum), hands (particularly proximal implanted thumbs) and genital anomalies (micropenis, hypospadias). We report here on four de novo cases having 2.5-6.1 Mb deletions involving 15q24: one 15q23q24.2 (Patient 1) and three 15q24.1q24.2 deletions (Patients 2-4). We correlate phenotype to genotype according to molecular boundaries of these deletions. Since bilateral iris coloboma and severe ano-rectal malformation were only present in Patient 1, we could link these anomalies to haploinsufficiency of 15q23 genes. Neither hypospadias nor micropenis were present in Patient 3 bearing the smallest deletion, therefore we could define 500 kb 15q24.1 region linked to these anomalies.
Figures

References
-
- Cushman LJ, Torres-Martinez W, Cherry AM, Manning MA, Abdul-Rahman O, Anderson CE, Punnett HH, Thurston VC, Sweeney D, Vance GH. A report of three patients with an interstitial deletion of chromosome 15q24. Am J Med Genet Part A. 2005;137A:65–71. - PubMed
-
- Formiga LD, Poenaru L, Couronne F, Flori E, Eibel JL, Deminatti MM, Savary JB, Lai JL, Gilgenkrantz S, Pierson M. Interstitial deletion of chromosome 15: two cases. Hum Genet. 1988;80:401–404. - PubMed
-
- Hassa PO, Hottiger MO. The diverse biological roles of mammalian PARPS, a small but powerful family of poly-ADP-ribose polymerases. Front Biosci. 2008;13:3046–3082. - PubMed
-
- Maruyama T, Matsuura M, Suzuki K, Yamamoto N. Cooperative activity of multiple upper layer proteins for thalamocortical axon growth. Dev Neurobiol. 2008;68:317–331. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

