Calcineurin inhibitors affect B cell antibody responses indirectly by interfering with T cell help
- PMID: 19922499
- PMCID: PMC2810388
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2009.04051.x
Calcineurin inhibitors affect B cell antibody responses indirectly by interfering with T cell help
Abstract
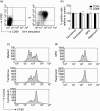
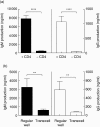
In general, humoral immune responses depend critically upon T cell help. In transplantation, prevention or treatment of humoral rejection therefore require drugs that ideally inhibit both B cell and T helper cell activity. Here, we studied the effects of commonly used immunosuppressive drugs [tacrolimus, cyclosporin, mycophenolic acid (MPA) and rapamycin] on T cell helper activity and on T cell-dependent B cell responses. T cells were activated polyclonally in the presence of immunosuppressive drugs in order to analyse the effect of these drugs on T cell proliferation, co-stimulatory ligand expression and cytokines. The impact of immunosuppressive drugs on T cell-dependent immunoglobulin production by B cells was addressed in T-B cell co-cultures. All drugs affected T cell proliferation and attenuated T cell co-stimulatory ligand (CD154 and CD278) expression when T cells were activated polyclonally. Tacrolimus, cyclosporin and rapamycin also attenuated B cell stimulatory cytokine mRNA levels in T cells. As a consequence, a decrease in immunoglobulin levels was observed in autologous T-B cell co-cultures, where T cell help is essential for immunoglobulin production. In contrast, when pre-activated T cells were used to stimulate autologous B cells, calcineurin inhibitors failed to inhibit B cell immunoglobulin production, whereas MPA and rapamycin did show inhibition. From these studies, it is evident that calcineurin inhibitors affect the humoral immune response by interfering with T helper signals, but not by targeting B cells directly. Furthermore, our studies support the necessity of intervening in T cell helper function to attenuate humoral responses.
Figures


References
-
- Patel R, Terasaki PI. Significance of the positive crossmatch test in kidney transplantation. N Engl J Med. 1969;280:735–9. - PubMed
-
- Joosten SA, Sijpkens YW, van Kooten C, Paul LC. Chronic renal allograft rejection: pathophysiologic considerations. Kidney Int. 2005;68:1–13. - PubMed
-
- Lee PC, Terasaki PI, Takemoto SK, et al. All chronic rejection failures of kidney transplants were preceded by the development of HLA antibodies. Transplantation. 2002;74:1192–4. - PubMed
-
- Mauiyyedi S, Pelle PD, Saidman S, et al. Chronic humoral rejection: identification of antibody-mediated chronic renal allograft rejection by C4d deposits in peritubular capillaries. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2001;12:574–82. - PubMed
-
- Hardy MA, Nowygrod R, Elberg A, Appel G. Use of ATG in treatment of steroid-resistant rejection. Transplantation. 1980;29:162–4. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

