Human papillomavirus type 8 E2 protein unravels JunB/Fra-1 as an activator of the beta4-integrin gene in human keratinocytes
- PMID: 19923172
- PMCID: PMC2812352
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01220-09
Human papillomavirus type 8 E2 protein unravels JunB/Fra-1 as an activator of the beta4-integrin gene in human keratinocytes
Abstract
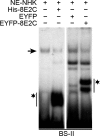
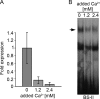
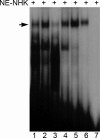
The papillomavirus life cycle parallels keratinocyte differentiation in stratifying epithelia. We have previously shown that the human papillomavirus type 8 (HPV8) E2 protein downregulates beta4-integrin expression in normal human keratinocytes, which may trigger subsequent differentiation steps. Here, we demonstrate that the DNA binding domain of HPV8 E2 is sufficient to displace a cellular factor from the beta4-integrin promoter. We identified the E2-displaceable factor as activator protein 1 (AP-1), a heteromeric transcription factor with differentiation-specific expression in the epithelium. beta4-Integrin-positive epithelial cells displayed strong AP-1 binding activity. Both AP-1 binding activity and beta4-integrin expression were coregulated during keratinocyte differentiation suggesting the involvement of AP-1 in beta4-integrin expression. In normal human keratinocytes the AP-1 complex was composed of JunB and Fra-1 subunits. Chromatin immunoprecipitation assays confirmed that JunB/Fra-1 proteins interact in vivo with the beta4-integrin promoter and that JunB/Fra-1 promoter occupancy is reduced during keratinocyte differentiation as well as in HPV8 E2 positive keratinocytes. Ectopic expression of the tethered JunB/Fra-1 heterodimer in normal human keratinocytes activated the beta4-integrin promoter, while coexpression of HPV8 E2 reverted the JunB/Fra-1 effect. In summary, we identified a novel mechanism of human beta4-integrin regulation that is specifically targeted by the HPV8 E2 protein mimicking transcriptional conditions of differentiation. This may explain the early steps of how HPV8 commits its host cells to the differentiation process required for the viral life cycle.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The human papillomavirus type 8 E2 protein suppresses beta4-integrin expression in primary human keratinocytes.J Virol. 2004 Oct;78(19):10738-46. doi: 10.1128/JVI.78.19.10738-10746.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 15367640 Free PMC article.
-
Differentiation of mouse keratinocytes is accompanied by PKC-dependent changes in AP-1 proteins.Oncogene. 1996 Jul 4;13(1):167-76. Oncogene. 1996. PMID: 8700543
-
Cholesterol sulfate stimulates involucrin transcription in keratinocytes by increasing Fra-1, Fra-2, and Jun D.J Lipid Res. 2001 Mar;42(3):390-8. J Lipid Res. 2001. PMID: 11254751
-
Integrin beta4, keratinocytes and papillomavirus infection.Int J Mol Med. 2006 Feb;17(2):195-202. Int J Mol Med. 2006. PMID: 16391815 Review.
-
Jun signalling in the epidermis: From developmental defects to psoriasis and skin tumors.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2006;38(7):1043-9. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2005.11.011. Epub 2005 Dec 20. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16423552 Review.
Cited by
-
HPV16-E2 protein modifies self-renewal and differentiation rate in progenitor cells of human immortalized keratinocytes.Virol J. 2017 Apr 3;14(1):65. doi: 10.1186/s12985-017-0736-2. Virol J. 2017. PMID: 28372578 Free PMC article.
-
The papillomavirus E2 proteins.Virology. 2013 Oct;445(1-2):57-79. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2013.06.006. Epub 2013 Jul 10. Virology. 2013. PMID: 23849793 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cross-talk of cutaneous beta human papillomaviruses and the immune system: determinants of disease penetrance.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2019 May 27;374(1773):20180287. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2018.0287. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30955489 Free PMC article. Review.
-
γ-Propoxy-Sulfo-Lichenan Induces In Vitro Cell Differentiation of Human Keratinocytes.Molecules. 2019 Feb 5;24(3):574. doi: 10.3390/molecules24030574. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 30764551 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of Brd4 in different steps of the papillomavirus life cycle.Virus Res. 2017 Mar 2;231:76-82. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2016.12.006. Epub 2016 Dec 10. Virus Res. 2017. PMID: 27965149 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Angel, P., A. Szabowski, and M. Schorpp-Kistner. 2001. Function and regulation of AP-1 subunits in skin physiology and pathology. Oncogene 20:2413-2423. - PubMed
-
- Behren, A., C. Simon, R. M. Schwab, E. Loetzsch, S. Brodbeck, E. Huber, F. Stubenrauch, H. P. Zenner, and T. Iftner. 2005. Papillomavirus E2 protein induces expression of the matrix metalloproteinase-9 via the extracellular signal-regulated kinase/activator protein-1 signaling pathway. Cancer Res. 65:11613-11621. - PubMed
-
- Blachon, S., and C. Demeret. 2003. The regulatory E2 proteins of human genital papillomaviruses are proapoptotic. Biochimie 85:813-819. - PubMed
-
- Boeckle, S., H. Pfister, and G. Steger. 2002. A new cellular factor recognizes E2 binding sites of papillomaviruses which mediate transcriptional repression by E2. Virology 293:103-117. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

