Early events in Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus infection of target cells
- PMID: 19923183
- PMCID: PMC2820927
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01334-09
Early events in Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus infection of target cells
Abstract
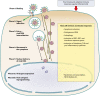
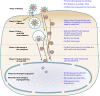
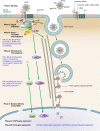
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV), the most recently identified member of the herpesvirus family, infects a variety of target cells in vitro and in vivo. This minireview surveys current information on the early events of KSHV infection, including virus-receptor interactions, involved envelope glycoproteins, mode of entry, intracellular trafficking, and initial viral and host gene expression programs. We describe data supporting the hypothesis that KSHV manipulates preexisting host cell signaling pathways to allow successful infection. The various signaling events triggered by infection, and their potential roles in the different stages of infection and disease pathogenesis, are summarized.
Figures
References
-
- Akula, S. M., P. P. Naranatt, F. Z. Wang, and B. Chandran. 2001. Human herpesvirus envelope-associated glycoprotein B interacts with heparan sulfate-like moieties. Virology 284:235-249. - PubMed
-
- Akula, S. M., F. Z. Wang, J. Vieira, and B. Chandran. 2001. Human herpesvirus 8 interaction with target cells involves heparan sulfate. Virology 282:245-255. - PubMed
-
- Akula, S. M., P. P. Naranatt, F. Z. Wang, and B. Chandran. 2002. Integrin α3β1 (CD49c/29) is a cellular receptor for Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV/HHV8) entry into target cells. Cell 108:407-419. - PubMed
-
- Baghian, A., M. Luftig, J. B. Black, Y. X. Meng, C. P. Pau, T. Voss, P. E. Pellett, and K. G. Kousoulas. 2000. Glycoprotein B of human herpesvirus 8 is a component of the virion in a cleaved form composed of amino- and carboxyl-terminal fragments. Virology 269:18-25. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

