The endoplasmic reticulum chaperone Cosmc directly promotes in vitro folding of T-synthase
- PMID: 19923218
- PMCID: PMC2807302
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.065169
The endoplasmic reticulum chaperone Cosmc directly promotes in vitro folding of T-synthase
Abstract
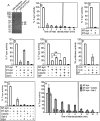
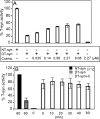
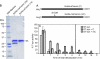
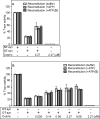
The T-synthase is the key beta 3-galactosyltransferase essential for biosynthesis of core 1 O-glycans (Gal beta 1-3GalNAc alpha 1-Ser/Thr) in animal cell glycoproteins. Here we describe the novel ability of an endoplasmic reticulum-localized molecular chaperone termed Cosmc to specifically interact with partly denatured T-synthase in vitro to cause partial restoration of activity. By contrast, a mutated form of Cosmc observed in patients with Tn syndrome has reduced chaperone function. The chaperone activity of Cosmc is specific, does not require ATP in vitro, and is effective toward T-synthase but not another beta-galactosyltransferase. Cosmc represents the first ER chaperone identified to be required for folding of a glycosyltransferase.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Functional assays for the molecular chaperone cosmc.Methods Enzymol. 2010;479:107-22. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(10)79006-6. Methods Enzymol. 2010. PMID: 20816162
-
Tight complex formation between Cosmc chaperone and its specific client non-native T-synthase leads to enzyme activity and client-driven dissociation.J Biol Chem. 2012 May 4;287(19):15317-29. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.312587. Epub 2012 Mar 13. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22416136 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a novel protein binding motif within the T-synthase for the molecular chaperone Cosmc.J Biol Chem. 2014 Apr 25;289(17):11630-11641. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.555870. Epub 2014 Mar 10. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24616093 Free PMC article.
-
The Cosmc connection to the Tn antigen in cancer.Cancer Biomark. 2014 Jan 1;14(1):63-81. doi: 10.3233/CBM-130375. Cancer Biomark. 2014. PMID: 24643043 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tumor-associated antigens: Tn antigen, sTn antigen, and T antigen.HLA. 2016 Dec;88(6):275-286. doi: 10.1111/tan.12900. Epub 2016 Sep 28. HLA. 2016. PMID: 27679419 Review.
Cited by
-
A testis-specific regulator of complex and hybrid N-glycan synthesis.J Cell Biol. 2010 Sep 6;190(5):893-910. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201004102. Epub 2010 Aug 30. J Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20805325 Free PMC article.
-
Glycosylation in cancer: mechanisms and clinical implications.Nat Rev Cancer. 2015 Sep;15(9):540-55. doi: 10.1038/nrc3982. Epub 2015 Aug 20. Nat Rev Cancer. 2015. PMID: 26289314 Review.
-
Cosmc deficiency causes spontaneous autoimmunity by breaking B cell tolerance.Sci Adv. 2021 Oct 8;7(41):eabg9118. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abg9118. Epub 2021 Oct 6. Sci Adv. 2021. PMID: 34613773 Free PMC article.
-
Mucin-Type O-GalNAc Glycosylation in Health and Disease.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021;1325:25-60. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-70115-4_2. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021. PMID: 34495529
-
The Breast Cancer-Associated Glycoforms of MUC1, MUC1-Tn and sialyl-Tn, Are Expressed in COSMC Wild-Type Cells and Bind the C-Type Lectin MGL.PLoS One. 2015 May 7;10(5):e0125994. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0125994. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25951175 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Helenius A., Marquardt T., Braakman I. (1992) Trends Cell Biol. 2, 227–231 - PubMed
-
- Hebert D. N., Molinari M. (2007) Physiol. Rev. 87, 1377–1408 - PubMed
-
- Ellgaard L., Helenius A. (2003) Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 4, 181–191 - PubMed
-
- Anfinsen C. B. (1973) Science 181, 223–230 - PubMed
-
- Fink A. L. (1999) Physiol. Rev. 79, 425–449 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

