Factors affecting recovery of Strongyloides stercoralis larvae: an approach to a newly modified formalin-ether concentration technique for diagnosis of strongyloidiasis
- PMID: 19923489
- PMCID: PMC2812279
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.01613-09
Factors affecting recovery of Strongyloides stercoralis larvae: an approach to a newly modified formalin-ether concentration technique for diagnosis of strongyloidiasis
Abstract
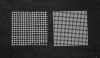
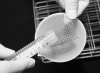
To improve the diagnosis efficiency of human strongyloidiasis by using formalin-ether concentration technique (FECT), the effects of various factors on the recovery rates of Strongyloides stercoralis larvae were comparatively evaluated. Fresh stool and a short time exposure of larvae to formalin yielded significantly higher numbers of larvae than preserved stool and 10-min exposure. Likewise, straining through wire mesh yielded a significantly higher number of larvae recovered than straining through gauze did. In addition, centrifugation for 5 min for separation of larvae from debris yielded a significantly greater number of larvae recovered than centrifugation for 2 min did. The efficacies of the five versions of FECT with different factors--FECT 1, FECT 2, FECT 3, FECT 4, and FECT 5--were then compared. It was found that FECT 5 was 1.8, 2.0, 1.9, and 1.4 times more effective than FECT 1, FECT 2, FECT 3, and FECT 4, respectively. FECT 5 is a modified FECT method, whose modifications included using fresh stool without a preservative substance; a short-time rather than 10-min formalin exposure; and the use of wire mesh instead of gauze.
Figures
References
-
- Arakaki, T., M. Iwanaga, F. Kinjo, A. Saito, R. Asato, and T. Ikeshiro. 1990. Efficacy of agar plate culture in detection of Strongyloides stercoralis infection. J. Parasitol. 76:425-428. - PubMed
-
- Beaver, P. C., R. C. Jung, and E. W. Cupp. 1984. Examination of specimens for parasites, p. 733-758. In P. C. Beaver, R. C. Jung, and E. W. Cupp (ed.). Clinical parasitology, 9th ed. Lea & Febiger, Philadelphia, PA.
-
- Clavel, A., A. Arnal, E. Sanchez, M. Varea, J. Quilez, I. Ramirez, and F. J. Castillo. 1996. Comparison of 2 centrifugation procedures in the formalin-ethyl acetate stool concentration technique for the detection of Cryptosporidium oocysts. Int. J. Parasitol. 26:671-672. - PubMed
-
- Grove, D. I. (ed.). 1989. Diagnosis, p. 175-197. In D. I. Grove (ed.), Strongyloidiasis: a major roundworm infection of man. Taylor & Francis, Philadelphia, PA.
-
- Grove, D. I. 1996. Human strongyloidiasis. Adv. Parasitol. 38:251-309. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources