A phase 2 multiple ascending dose trial of bapineuzumab in mild to moderate Alzheimer disease
- PMID: 19923550
- PMCID: PMC2790221
- DOI: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181c67808
A phase 2 multiple ascending dose trial of bapineuzumab in mild to moderate Alzheimer disease
Abstract
Background: Bapineuzumab, a humanized anti-amyloid-beta (Abeta) monoclonal antibody for the potential treatment of Alzheimer disease (AD), was evaluated in a multiple ascending dose, safety, and efficacy study in mild to moderate AD.
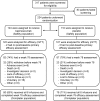
Methods: The study enrolled 234 patients, randomly assigned to IV bapineuzumab or placebo in 4 dose cohorts (0.15, 0.5, 1.0, or 2.0 mg/kg). Patients received 6 infusions, 13 weeks apart, with final assessments at week 78. The prespecified primary efficacy analysis in the modified intent-to-treat population assumed linear decline and compared treatment differences within dose cohorts on the Alzheimer's Disease Assessment Scale-Cognitive and Disability Assessment for Dementia. Exploratory analyses combined dose cohorts and did not assume a specific pattern of decline.
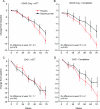
Results: No significant differences were found in the primary efficacy analysis. Exploratory analyses showed potential treatment differences (p < 0.05, unadjusted for multiple comparisons) on cognitive and functional endpoints in study "completers" and APOE epsilon4 noncarriers. Reversible vasogenic edema, detected on brain MRI in 12/124 (9.7%) bapineuzumab-treated patients, was more frequent in higher dose groups and APOE epsilon4 carriers. Six vasogenic edema patients were asymptomatic; 6 experienced transient symptoms.
Conclusions: Primary efficacy outcomes in this phase 2 trial were not significant. Potential treatment differences in the exploratory analyses support further investigation of bapineuzumab in phase 3 with special attention to APOE epsilon4 carrier status.
Classification of evidence: Due to varying doses and a lack of statistical precision, this Class II ascending dose trial provides insufficient evidence to support or refute a benefit of bapineuzumab.
Figures
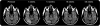
Comment in
-
APOE {epsilon}4 and bapineuzumab: Infusing pharmacogenomics into Alzheimer disease therapeutics.Neurology. 2009 Dec 15;73(24):2052-3. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181c6784a. Epub 2009 Nov 18. Neurology. 2009. PMID: 19923549 No abstract available.
-
A phase 2 multiple ascending dose trial of bapineuzumab in mild to moderate Alzheimer disease.Neurology. 2010 Jun 15;74(24):2026; author reply 2026-7. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181e03844. Neurology. 2010. PMID: 20548049 No abstract available.
References
-
- Selkoe DJ, Schenk D. Alzheimer's disease: molecular understanding predicts amyloid-based therapeutics. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 2003;43:545–584. - PubMed
-
- Bard F, Cannon C, Barbour R, et al. Peripherally administered antibodies against amyloid beta-peptide enter the central nervous system and reduce pathology in a mouse model of Alzheimer disease. Nat Med 2000;6:916–919. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P50-AG005134/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 NS15655/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- 1U01AG032438-01/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG08671/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- 1 R01 MH58620-01A2/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P50AG08702/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG017761/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R43AG033474/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG14763/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- 1-UO1-AG024904/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG019610/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG026114/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- G0801306/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- AG08671/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- 1RL1AA017536-01/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- P01AG07232/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG016976/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005136/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG06036-13/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U54RR024350-01/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG024904/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01-AG16976/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG027435/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS042859/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- 1 R03 AG023916-01A1/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- UO1AGO24904/PHS HHS/United States
- R01HL091099/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P50MH068789/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- 1-R01-AG030457-01A1/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- 5-U01-AG10483/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 NS007224-19/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG007370/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P20 RR020626/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- IR21DK062098/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG030004-01/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AF10483/AF/ACF HHS/United States
- P30 P3-AG 019610/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- G0601846/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
