Identification of Western equine encephalitis virus structural proteins that confer protection after DNA vaccination
- PMID: 19923571
- PMCID: PMC2812089
- DOI: 10.1128/CVI.00377-09
Identification of Western equine encephalitis virus structural proteins that confer protection after DNA vaccination
Abstract
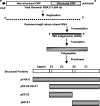
DNA vaccines encoding different portions of the structural proteins of western equine encephalitis virus were tested for the efficacy of their protection in a 100% lethal mouse model of the virus. The 6K-E1 structural protein encoded by the DNA vaccine conferred complete protection against challenge with the homologous strain and limited protection against challenge with a heterologous strain.
Figures


References
-
- Das, D., S. L. Gares, L. P. Nagata, and M. R. Suresh. 2004. Evaluation of a western equine encephalitis recombinant E1 protein for protective immunity and diagnostics. Antivir. Res. 64:85-92. - PubMed
-
- Doria-Rose, N. A., and N. L. Haigwood. 2003. DNA vaccine strategies: candidates for immune modulation and immunization regimens. Methods 31:207-216. - PubMed
-
- Griffin, D. E. 2007. Alphaviruses, p. 1023-1067. In D. M. Knipe and P. M. Howley (ed.), Fields virology, vol. 1, 5th ed. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia, PA.
-
- Hodgson, L. A., G. V. Ludwig, and J. F. Smith. 1999. Expression, processing, and immunogenicity of the structural proteins of Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus from recombinant baculovirus vectors. Vaccine 17:1151-1160. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

