Structure of an N-terminally truncated Nudix hydrolase DR2204 from Deinococcus radiodurans
- PMID: 19923723
- PMCID: PMC2777031
- DOI: 10.1107/S1744309109037191
Structure of an N-terminally truncated Nudix hydrolase DR2204 from Deinococcus radiodurans
Abstract
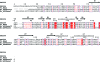
Nudix pyrophosphatases are a well represented protein family in the Deinococcus radiodurans genome. These hydrolases, which are known to be enzymatically active towards nucleoside diphosphate derivatives, play a role in cleansing the cell pool of potentially deleterious damage products. Here, the structure of DR2204, the only ADP-ribose pyrophosphatase in the D. radiodurans genome that is known to be active towards flavin adenosine dinucleotide (FAD), is presented at 2.0 angstrom resolution.
Figures
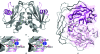
References
-
- Abrahams, J. P. & Leslie, A. G. W. (1996). Acta Cryst. D52, 30–42. - PubMed
-
- Battista, J. R. (1997). Annu. Rev. Microbiol.51, 203–224. - PubMed
-
- Bessman, M. J., Frick, D. N. & O’Handley, S. F. (1996). J. Biol. Chem.271, 25059–25062. - PubMed
-
- Bhatnagar, S. K. & Bessman, M. J. (1988). J. Biol. Chem.263, 8953–8957. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

