Natural killer cells and cancer: regulation by the killer cell Ig-like receptors (KIR)
- PMID: 19923897
- PMCID: PMC2825280
- DOI: 10.4161/cbt.8.23.10455
Natural killer cells and cancer: regulation by the killer cell Ig-like receptors (KIR)
Abstract
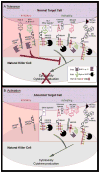
Natural killer (NK) cells are innate immune effector cells that make up approximately 10-15% of the peripheral blood lymphocytes in humans and are primarily involved in immunosurveillance to eliminate transformed and virally-infected cells. They were originally defined by their ability to spontaneously eliminate rare cells lacking expression of class I major histocompatibility complex (MHC-I) self molecules, which is commonly referred to as "missing self" recognition. The molecular basis for missing self recognition emerges from the expression of MHC-I-specific inhibitory receptors on the NK cell surface that tolerize NK cells toward normal MHC-I-expressing cells. By lacking inhibitory receptor ligands, tumor cells or virus-infected cells that have down-modulated surface MHC-I expression become susceptible to attack by NK cells. Killer cell Ig-like receptors (KIR; CD158) constitute a family of MHC-I binding receptors that plays a major role in regulating the activation thresholds of NK cells and some T cells in humans. Here, we review the multiple levels of KIR diversity that contribute to the generation of a highly varied NK cell repertoire and explain how this diversity can influence susceptibility to a variety of diseases, including cancer. We further describe strategies by which KIR can be manipulated therapeutically to treat cancer, through the exploitation of KIR/MHC-I ligand mismatch to potentiate hematopoietic stem cell transplantation and the use of KIR blockade to enhance tumor cell killing.
Figures

References
-
- Biron CA. Activation and function of natural killer cell responses during viral infections. Curr Opin Immunol. 1997;9:24–34. - PubMed
-
- Wu J, Lanier LL. Natural killer cells and cancer. Adv Cancer Res. 2003;90:127–56. - PubMed
-
- Smyth MJ, Cretney E, Kelly JM, Westwood JA, Street SE, Yagita H, et al. Activation of NK cell cytotoxicity. Mol Immunol. 2005;42:501–10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
