High-performance liquid chromatographic quantification of flavonoids in Eriocaulaceae species and their antimicrobial activity
- PMID: 19924092
- PMCID: PMC6254972
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules14114644
High-performance liquid chromatographic quantification of flavonoids in Eriocaulaceae species and their antimicrobial activity
Abstract
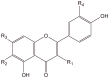
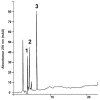
Quantification of prepared samples by analysis using high performance liquid chromatography with DAD detection was developed to analyze rutin, 6-methoxyapigenin, and 6-methoxyapigenin-7-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside isolated from methanolic extracts of different genus: Syngonanthus, Leiothix and Eriocaulon (Eriocaulaceae). The linearity, accuracy, and the inter-day precision of the procedure were evaluated. The calibration curves were linear. The recoveries of the flavonoids in the samples analyzed were 96.3% to 98.5%. The percentage coefficient of variation for the quantitative analysis of the flavonoids in the analyses of the samples was under 5%. The antimicrobial activity of the five methanol extracts of these Eriocaulaceae species was assayed against the microorganisms Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Escherichia coli, Salmonella setubal, Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Candida albicans. Measured MIC values ranged from 1.25 to 10.00 mg/mL. The flavonoid contents suggest that Eriocaulaceae species may be a promising source of compounds to produce natural phytomedicines.
Figures
References
-
- Giulietti A.M., Amaral M.C., Bittrich V. Phylogenetic analysis of inter and infrageneric relationships of Leiothrix Ruhl. (Eriocaulaceae) Kew Bull. 1995;50:55–71. doi: 10.2307/4114608. - DOI
-
- Dokkedal A.L., Salatino A. Chemistry in Paepalanthus and taxonomic implications. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 1992;20:31–32. doi: 10.1016/0305-1978(92)90069-P. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

