Photoreceptor responses of fruitflies with normal and reduced arrestin content studied by simultaneous measurements of visual pigment fluorescence and ERG
- PMID: 19924417
- PMCID: PMC2797847
- DOI: 10.1007/s00359-009-0489-5
Photoreceptor responses of fruitflies with normal and reduced arrestin content studied by simultaneous measurements of visual pigment fluorescence and ERG
Abstract
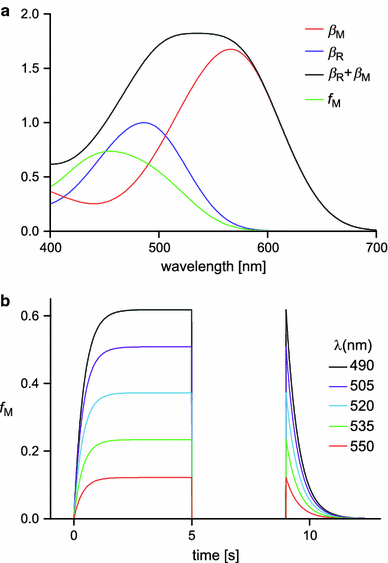
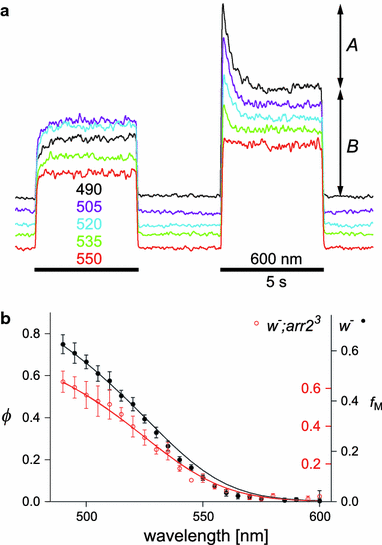
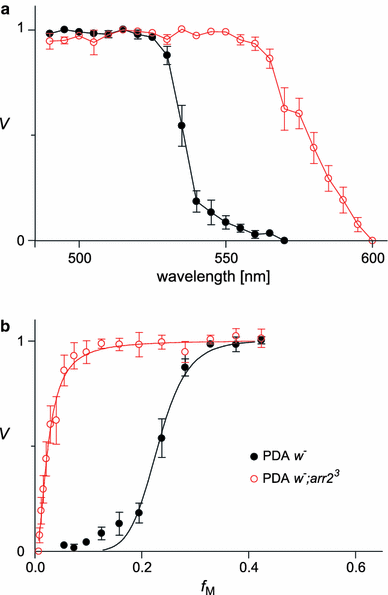
We have simultaneously measured the electroretinogram (ERG) and the metarhodopsin content via fluorescence in white-eyed, wild-type Drosophila and the arrestin2 hypomorphic mutant (w(-);arr2 (3)) at a range of stimulus wavelengths and intensities. Photoreceptor response amplitude and termination (transition between full repolarization and prolonged depolarizing afterpotential, PDA) were related to visual pigment conversions and arrestin concentration. The data were implemented in a kinetic model of the rhodopsin-arrestin cycle, allowing us to estimate the active metarhodopsin concentration as a function of effective light intensity and arrestin concentration. Arrestin reduction in the mutant modestly increased the light sensitivity and decreased the photoreceptor dynamic range. Compared to the wild type, in the mutant the transition between full repolarization and PDA occurred at a lower metarhodopsin fraction and was more abrupt. We developed a steady-state stochastic model to interpret the dependence of the PDA on effective light intensity and arrestin content and to help deduce the arrestin to rhodopsin ratio from the sensitivity and PDA data. The feasibility of different experimental methods for the estimation of arrestin content from ERG and PDA is discussed.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Metarhodopsin control by arrestin, light-filtering screening pigments, and visual pigment turnover in invertebrate microvillar photoreceptors.J Comp Physiol A Neuroethol Sens Neural Behav Physiol. 2011 Mar;197(3):227-41. doi: 10.1007/s00359-010-0604-7. Epub 2010 Nov 3. J Comp Physiol A Neuroethol Sens Neural Behav Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21046112 Free PMC article.
-
Light-induced translocation of Drosophila visual Arrestin2 depends on Rac2.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Mar 9;107(10):4740-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0906386107. Epub 2010 Feb 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20176938 Free PMC article.
-
A role for the light-dependent phosphorylation of visual arrestin.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999 May 25;96(11):6072-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.11.6072. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999. PMID: 10339543 Free PMC article.
-
PDA (prolonged depolarizing afterpotential)-defective mutants: the story of nina's and ina's--pinta and santa maria, too.J Neurogenet. 2012 Jun;26(2):216-37. doi: 10.3109/01677063.2011.642430. Epub 2012 Jan 27. J Neurogenet. 2012. PMID: 22283778 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The history of the prolonged depolarizing afterpotential (PDA) and its role in genetic dissection of Drosophila phototransduction.J Neurogenet. 2012 Jun;26(2):106-17. doi: 10.3109/01677063.2012.666299. Epub 2012 Mar 20. J Neurogenet. 2012. PMID: 22428622 Review.
Cited by
-
Arrestin translocation is stoichiometric to rhodopsin isomerization and accelerated by phototransduction in Drosophila photoreceptors.Neuron. 2010 Sep 23;67(6):997-1008. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2010.08.024. Neuron. 2010. PMID: 20869596 Free PMC article.
-
Functional interplay of visual, sensitizing and screening pigments in the eyes of Drosophila and other red-eyed dipteran flies.J Physiol. 2017 Aug 15;595(16):5481-5494. doi: 10.1113/JP273674. Epub 2017 Apr 11. J Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28295348 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Autofluorescent Biomolecules in Diptera: From Structure to Metabolism and Behavior.Molecules. 2022 Jul 12;27(14):4458. doi: 10.3390/molecules27144458. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35889334 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metarhodopsin control by arrestin, light-filtering screening pigments, and visual pigment turnover in invertebrate microvillar photoreceptors.J Comp Physiol A Neuroethol Sens Neural Behav Physiol. 2011 Mar;197(3):227-41. doi: 10.1007/s00359-010-0604-7. Epub 2010 Nov 3. J Comp Physiol A Neuroethol Sens Neural Behav Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21046112 Free PMC article.
-
Noise-robust recognition of wide-field motion direction and the underlying neural mechanisms in Drosophila melanogaster.Sci Rep. 2015 May 14;5:10253. doi: 10.1038/srep10253. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 25974721 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cosens DJ, Briscoe D. A switch phenomenon in the compound eye of the white-eyed mutant of Drosophila melanogaster. J Insect Physiol. 1972;18:627–632. doi: 10.1016/0022-1910(72)90190-4. - DOI
-
- Dartnall HJA. Photosensitivity. In: Dartnall HJA, editor. Handbook of sensory physiology, vol VII/1. Berlin: Springer; 1972. pp. 122–145.
-
- Dempster J (2001) The laboratory computer: a guide for neuroscientists and physiologists, Academic Press, New York
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

