A combined method of laser capture microdissection and X-Gal histology to analyze gene expression in c-Fos-specific neurons
- PMID: 19925827
- PMCID: PMC2829768
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2009.11.011
A combined method of laser capture microdissection and X-Gal histology to analyze gene expression in c-Fos-specific neurons
Abstract
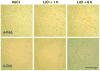
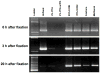
c-Fos is a member of the activator protein 1 family that regulates transcription of target genes. c-Fos is transiently induced in specific regions of the brain after a variety of external stimuli including learning and memory formation. Analysis of gene expression in c-Fos-expressing cells of the brain may help identify target genes that play important roles in synaptic strength or neuronal morphology. In the present study, we developed a combined method of laser capture microdissection and 5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indoly-beta-D-galactopyranosidase (X-Gal) histology to analyze gene expression in stimulus-induced c-Fos-positive cells. Using transgenic mice carrying a c-fos-lacZ fusion gene, c-Fos-positive cells were easily identified by measuring of beta-galactosidase (beta-Gal) activity. To establish the fidelity of the reporter transgene, the time course of endogenous c-Fos and the c-fos-lacZ transgene expression in the amygdala induced by LiCl administration was investigated by immunohistochemistry and X-Gal staining. LiCl increased the numbers of c-Fos- and beta-Gal-positive cells in the central and basolateral amygdala of the transgenic mice. To ensure that RNA was preserved in X-Gal stained tissue sections, different fixations were examined, with the conclusion that ethanol fixation was best for both RNA preservation and X-Gal staining quality. Finally, in combining X-Gal staining, single-cell LCM and RT-PCR, we confirmed mRNA expression of endogenous c-fos and beta-actin genes in LiCl-induced beta-Gal-positive cells in the CeA, cortex and hippocampus. Combining LCM and transgenic reporter genes provides a powerful tool with which to investigate tissue- or cell-specific gene expression.
Copyright 2009 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Visualization of functionally activated circuitry in the brain.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Mar 5;99(5):3252-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.042701199. Epub 2002 Feb 26. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002. PMID: 11867719 Free PMC article.
-
Beta-galactosidase staining in the nucleus of the solitary tract of Fos-Tau-LacZ mice is unaffected by monosodium glutamate taste stimulation.PLoS One. 2014 Sep 5;9(9):e107238. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0107238. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25192442 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of AP-1 family transcription factors in the amygdala during conditioned taste aversion learning: role for Fra-2.Brain Res. 2008 May 1;1207:128-41. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2008.01.072. Epub 2008 Feb 9. Brain Res. 2008. PMID: 18374904 Free PMC article.
-
Overview and assessment of the histochemical methods and reagents for the detection of β-galactosidase activity in transgenic animals.Anat Sci Int. 2016 Jan;91(1):56-67. doi: 10.1007/s12565-015-0300-3. Epub 2015 Sep 22. Anat Sci Int. 2016. PMID: 26394634 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The X-gal caution in neural transplantation studies.Cell Transplant. 2000 Sep-Oct;9(5):657-67. doi: 10.1177/096368970000900510. Cell Transplant. 2000. PMID: 11144962 Review.
Cited by
-
Analysis of transcription factor mRNAs in identified oxytocin and vasopressin magnocellular neurons isolated by laser capture microdissection.PLoS One. 2013 Jul 24;8(7):e69407. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0069407. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23894472 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the memory: existing activity-dependent tools to tag and manipulate engram cells.Front Cell Neurosci. 2024 Jan 8;17:1279032. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2023.1279032. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38259503 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase in the amygdala plays a critical role in lithium chloride-induced taste aversion learning.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2012 Jan;97(1):132-9. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2011.10.005. Epub 2011 Nov 9. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2012. PMID: 22085719 Free PMC article.
-
An improved procedure for isolation of high-quality RNA from nematode-infected Arabidopsis roots through laser capture microdissection.Plant Methods. 2016 Apr 26;12:25. doi: 10.1186/s13007-016-0123-9. eCollection 2016. Plant Methods. 2016. PMID: 27123040 Free PMC article.
-
FACS identifies unique cocaine-induced gene regulation in selectively activated adult striatal neurons.J Neurosci. 2011 Mar 16;31(11):4251-9. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.6195-10.2011. J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21411666 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bhattacherjee V, Mukhopadhyay P, Singh S, Roberts E, Hackmiller R, Greene R, Pisano M. Laser capture microdissection of fluorescently labeled embryonic cranial neural crest cells. Genesis. 2004;39:58–64. - PubMed
-
- Bonner RF, Emmert-Buck M, Cole K, Pohida T, Chuaqui R, Goldstein S, Liotta LA. Laser capture microdissection: molecular analysis of tissue. Science. 1997;278:1481–1483. - PubMed
-
- Bravo R, Neuberg M, Burckhardt J, Almendral J, Wallich R, Müller R. Involvement of common and cell type-specific pathways in c-fos gene control: stable induction of cAMP in macrophages. Cell. 1987;48:251–60. - PubMed
-
- Chiu R, Boyle WJ, Meek J, Smeal T, Hunter T, Karin M. The c-Fos protein interacts with c-Jun/AP-1 to stimulate transcription of AP-1 responsive genes. Cell. 1988;54:541–2. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

