Imaging brain fatigue from sustained mental workload: an ASL perfusion study of the time-on-task effect
- PMID: 19925871
- PMCID: PMC2830749
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.11.020
Imaging brain fatigue from sustained mental workload: an ASL perfusion study of the time-on-task effect
Abstract
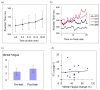
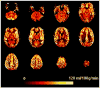
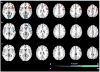
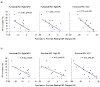
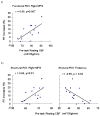
During sustained periods of a taxing cognitive workload, humans typically display time-on-task (TOT) effects, in which performance gets steadily worse over the period of task engagement. Arterial spin labeling (ASL) perfusion functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) was used in this study to investigate the neural correlates of TOT effects in a group of 15 subjects as they performed a 20-min continuous psychomotor vigilance test (PVT). Subjects displayed significant TOT effects, as seen in progressively slower reaction times and significantly increased mental fatigue ratings after the task. Perfusion data showed that the PVT activates a right lateralized fronto-parietal attentional network in addition to the basal ganglia and sensorimotor cortices. The fronto-parietal network was less active during post-task rest compared to pre-task rest, and regional CBF decrease in this network correlated with performance decline. These results demonstrate the persistent effects of cognitive fatigue in the fronto-parietal network after a period of heavy mental work and indicate the critical role of this attentional network in mediating TOT effects. Furthermore, resting regional CBF in the thalamus and right middle frontal gyrus prior to task onset was predictive of subjects' subsequent performance decline, suggesting that resting CBF quantified by ASL perfusion fMRI may be a useful indicator of performance potential and a marker of the level of fatigue in the neural attentional system.
Copyright 2009 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Abler B, Hofer C, Viviani R. Habitual emotion regulation strategies and baseline brain perfusion. Neuroreport. 2008;19:21–24. - PubMed
-
- Aguirre GK, Zarahn E, D'Esposito M. Empirical analyses of BOLD fMRI statistics. II. Spatially smoothed data collected under null-hypothesis and experimental conditions. Neuroimage. 1997;5:199–212. - PubMed
-
- Aguirre GK, Detre JA, Zarahn E, Alsop DC. Experimental design and the relative sensitivity of BOLD and perfusion fMRI. Neuroimage. 2002;15:488–500. - PubMed
-
- Arnedt JT, Owens J, Crouch M, Stahl J, Carskadon MA. Neurobehavioral performance of residents after heavy night call vs after alcohol ingestion. Jama. 2005;294:1025–1033. - PubMed
-
- Beschoner P, Richter S, Lo H, Sim EJ, Baron K, Osterfeld N, Horn AB, Viviani R. Baseline brain perfusion and working memory capacity: a neuroimaging study. Neuroreport. 2008;19:1803–1807. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

