Structures of RNA polymerase-antibiotic complexes
- PMID: 19926275
- PMCID: PMC2950656
- DOI: 10.1016/j.sbi.2009.10.010
Structures of RNA polymerase-antibiotic complexes
Abstract
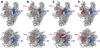
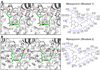
Inhibition of bacterial RNA polymerase (RNAP) is an established strategy for antituberculosis therapy and broad-spectrum antibacterial therapy. Crystal structures of RNAP-inhibitor complexes are available for four classes of antibiotics: rifamycins, sorangicin, streptolydigin, and myxopyronin. The structures define three different targets, and three different mechanisms, for inhibition of bacterial RNAP: (1) rifamycins and sorangicin bind near the RNAP active center and block extension of RNA products; (2) streptolydigin interacts with a target that overlaps the RNAP active center and inhibits conformational cycling of the RNAP active center; and (3) myxopyronin interacts with a target remote from the RNAP active center and functions by interfering with opening of the RNAP active-center cleft to permit entry and unwinding of DNA and/or by interfering with interactions between RNAP and the DNA template strand. The structures enable construction of homology models of pathogen RNAP-antibiotic complexes, enable in silico screening for new antibacterial agents, and enable rational design of improved antibacterial agents.
Figures


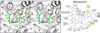
References
-
- Chopra I. Bacterial RNA polymerase: a promising target for the discovery of new antimicrobial agents. Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2007;8:600–607. - PubMed
-
- Darst SA. New inhibitors targeting bacterial RNA polymerase. Trends Biochem Sci. 2004;29:159–160. - PubMed
-
- Villain-Guillot P, Bastide L, Gualtieri M, Leonetti J. Progress in targeting bacterial transcription. Drug Discov Today. 2007;12:200–208. - PubMed
-
- Wehrli W. Ansamycins: chemistry, biosynthesis and biological activity. Top Curr Chem. 1977;72:21–49. - PubMed
-
- Floss HG, Yu TW. Rifamycin-mode of action, resistance, and biosynthesis. Chem Rev. 2005;105:621–632. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

