Simultaneous determination of labile proton concentration and exchange rate utilizing optimal RF power: Radio frequency power (RFP) dependence of chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) MRI
- PMID: 19926319
- PMCID: PMC2818407
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmr.2009.10.012
Simultaneous determination of labile proton concentration and exchange rate utilizing optimal RF power: Radio frequency power (RFP) dependence of chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) MRI
Abstract
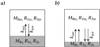
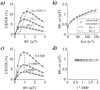
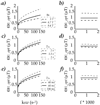
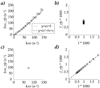
Chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) MRI is increasingly used to probe mobile proteins and microenvironment properties, and shows great promise for tumor and stroke diagnosis. However, CEST MRI contrast mechanism is complex, depending not only on the CEST agent concentration, exchange and relaxation properties, but also varying with experimental conditions such as magnetic field strength and RF power. Hence, it remains somewhat difficult to quantify apparent CEST MRI contrast for properties such as pH, temperature and protein content. In particular, CEST MRI is susceptible to RF spillover effects in that RF irradiation may directly saturate the bulk water MR signal, leading to an optimal RF power at which the CEST contrast is maximal. Whereas RF spillover is generally considered an adverse effect, it is noted here that the optimal RF power strongly varies with exchange rate, although with negligible dependence on labile proton concentration. An empirical solution suggested that optimal RF power may serve as a sensitive parameter for simultaneously determining the labile proton content and exchange rate, hence, allowing improved characterization of the CEST system. The empirical solution was confirmed by numerical simulation, and experimental validation is needed to further evaluate the proposed technique.
Copyright 2009 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A review of optimization and quantification techniques for chemical exchange saturation transfer MRI toward sensitive in vivo imaging.Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2015 May-Jun;10(3):163-178. doi: 10.1002/cmmi.1628. Epub 2015 Jan 12. Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2015. PMID: 25641791 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Simplified quantification of labile proton concentration-weighted chemical exchange rate (k(ws) ) with RF saturation time dependent ratiometric analysis (QUESTRA): normalization of relaxation and RF irradiation spillover effects for improved quantitative chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) MRI.Magn Reson Med. 2012 Apr;67(4):936-42. doi: 10.1002/mrm.23068. Epub 2011 Aug 12. Magn Reson Med. 2012. PMID: 21842497 Free PMC article.
-
Simultaneous experimental determination of labile proton fraction ratio and exchange rate with irradiation radio frequency power-dependent quantitative CEST MRI analysis.Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2013 May-Jun;8(3):246-51. doi: 10.1002/cmmi.1524. Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2013. PMID: 23606428 Free PMC article.
-
Simulation and optimization of pulsed radio frequency irradiation scheme for chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) MRI-demonstration of pH-weighted pulsed-amide proton CEST MRI in an animal model of acute cerebral ischemia.Magn Reson Med. 2011 Oct;66(4):1042-8. doi: 10.1002/mrm.22894. Epub 2011 Mar 24. Magn Reson Med. 2011. PMID: 21437977 Free PMC article.
-
Radiofrequency labeling strategies in chemical exchange saturation transfer MRI.NMR Biomed. 2023 Jun;36(6):e4944. doi: 10.1002/nbm.4944. Epub 2023 Apr 27. NMR Biomed. 2023. PMID: 37002814 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Quasi-steady-state CEST (QUASS CEST) solution improves the accuracy of CEST quantification: QUASS CEST MRI-based omega plot analysis.Magn Reson Med. 2021 Aug;86(2):765-776. doi: 10.1002/mrm.28744. Epub 2021 Mar 10. Magn Reson Med. 2021. PMID: 33749052 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative description of radiofrequency (RF) power-based ratiometric chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) pH imaging.NMR Biomed. 2015 May;28(5):555-65. doi: 10.1002/nbm.3284. Epub 2015 Mar 23. NMR Biomed. 2015. PMID: 25807919 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative pulsed CEST-MRI at a clinical 3T MRI system.MAGMA. 2017 Oct;30(5):505-516. doi: 10.1007/s10334-017-0625-0. Epub 2017 May 31. MAGMA. 2017. PMID: 28569374
-
A review of optimization and quantification techniques for chemical exchange saturation transfer MRI toward sensitive in vivo imaging.Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2015 May-Jun;10(3):163-178. doi: 10.1002/cmmi.1628. Epub 2015 Jan 12. Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2015. PMID: 25641791 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluating the use of a continuous approximation for model-based quantification of pulsed chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST).J Magn Reson. 2012 Sep;222(3):88-95. doi: 10.1016/j.jmr.2012.07.003. Epub 2012 Jul 16. J Magn Reson. 2012. PMID: 22858666 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Forsen S, Hoffman RA. Study of moderately rapid chemical exchange reactions by means of nuclear magnetic double resonance. J. Chem. Phys. 1963;39:2892–2901.
-
- Wolff SD, Balaban RS. NMR imaging of labile proton exchange. J. Magn. Reson. 1990;86:164–169.
-
- Ward KM, Aletras AH, Balaban RS. A new class of contrast agents for MRI based on proton chemical exchange dependent saturation transfer (CEST) J. Magn. Reson. 2000;143:79–87. - PubMed
-
- Aime S, Delli Castelli D, Fedeli F, Terreno E. A paramagnetic MRI-CEST agent responsive to lactate concentration. J Am Chem Soc. 2002;124:9364–9365. - PubMed
-
- Snoussi K, Bulte JWM, Gueron M, van Zijl PCM. Sensitive CEST agents based on nucleic acid imino proton exchange: detection of poly(rU) and of a dendrimer-poly(rU) model for nucleic acid delivery and pharmacology. Magn. Reson. Med. 2003;49:998–1005. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

