Toward rational design of electrical stimulation strategies for epilepsy control
- PMID: 19926525
- PMCID: PMC2818293
- DOI: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2009.10.017
Toward rational design of electrical stimulation strategies for epilepsy control
Abstract
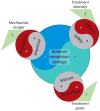
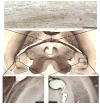
Electrical stimulation is emerging as a viable alternative for patients with epilepsy whose seizures are not alleviated by drugs or surgery. Its attractions are temporal and spatial specificity of action, flexibility of waveform parameters and timing, and the perception that its effects are reversible unlike resective surgery. However, despite significant advances in our understanding of mechanisms of neural electrical stimulation, clinical electrotherapy for seizures relies heavily on empirical tuning of parameters and protocols. We highlight concurrent treatment goals with potentially conflicting design constraints that must be resolved when formulating rational strategies for epilepsy electrotherapy, namely, seizure reduction versus cognitive impairment, stimulation efficacy versus tissue safety, and mechanistic insight versus clinical pragmatism. First, treatment markers, objectives, and metrics relevant to electrical stimulation for epilepsy are discussed from a clinical perspective. Then the experimental perspective is presented, with the biophysical mechanisms and modalities of open-loop electrical stimulation, and the potential benefits of closed-loop control for epilepsy.
2009 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
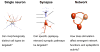
References
-
- Stevens JR. Clozapine: the Yin and Yang of seizures and psychosis. Biol Psychiatry. 1995;37(7):425–6. - PubMed
-
- Theodore WH, Fisher RS. Brain stimulation for epilepsy. Lancet Neurol. 2004;3(2):111–8. - PubMed
-
- Karceski S. Electrical stimulation devices in the treatment of epilepsy. Acta Neurochir Suppl. 2007;97(Pt 2):247–59. - PubMed
-
- Salanova V, Worth R. Neurostimulators in epilepsy. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2007;7(4):315–9. - PubMed
-
- Li Y, Mogul DJ. Electrical control of epileptic seizures. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2007;24(2):197–204. - PubMed

