Influence of lipophilicity on drug partitioning into sclera, choroid-retinal pigment epithelium, retina, trabecular meshwork, and optic nerve
- PMID: 19926800
- PMCID: PMC2835449
- DOI: 10.1124/jpet.109.161570
Influence of lipophilicity on drug partitioning into sclera, choroid-retinal pigment epithelium, retina, trabecular meshwork, and optic nerve
Retraction in
-
Re: Kadam RS and Kompella UB (2010) Influence of Lipophilicity on Drug Partitioning into Sclera, Choroid-Retinal Pigment Epithelium, Retina, Trabecular Meshwork, and Optic Nerve. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 332:1107-1120; doi:10.1124/jpet.109.161570.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2015 Feb;352(2):326. doi: 10.1124/jpet.114.02er15. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2015. PMID: 25542193 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
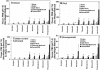
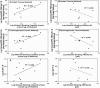
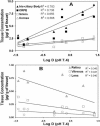
In vitro bovine eye tissue/phosphate-buffered saline, pH 7.4, partition coefficients (Kt:b), in vitro binding to natural melanin, and in vivo delivery at 1 h after posterior subconjunctival injection in Brown Norway rats were determined for eight beta-blockers. The Kt:b was in the order intact tissue, dry weight method >or= intact tissue, wet weight method corrected for tissue water and drug in tissue water >> intact tissue, wet weight method > homogenized tissue. In intact tissue methods, Kt:b followed the order choroid-retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) > trabecular meshwork > retina > sclera approximately optic nerve; propranolol > betaxolol > pindolol approximately timolol approximately metoprolol > sotalol approximately atenolol approximately nadolol. Intact tissue, wet weight log (Kt:b) correlated positively with log D for all tissues (R(2) of 0.7-0.9). Log (melanin binding capacity) correlated positively with choroid-RPE log (Kt:b) (R(2) of 0.5). With an increase in concentration, Kt:b decreased in trabecular meshwork for all beta-blockers and for some lipophilic beta-blockers in choroid-RPE and sclera. With an increase in drug lipophilicity, in vivo tissue distribution increased in choroid-RPE, iris-ciliary body, sclera, and cornea but exhibited a declining trend in retina, vitreous, and lens. In vitro bovine intact tissue, wet weight Kt:b correlated positively with rat in vivo tissue/vitreous humor distribution for sclera, choroid-RPE, and retina (R(2) of 0.985-0.993). In vitro tissue partition coefficients might be useful in predicting in vivo drug distribution after trans-scleral delivery. Less lipophilic solutes exhibiting limited nonproductive binding in choroid-RPE might exhibit greater trans-scleral delivery to the retina and vitreous.
Figures





Comment in
-
Findings of Research Misconduct.Fed Regist. 2018 Dec 6;83(234):62875. Fed Regist. 2018. PMID: 30556543 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Influence of drug solubility and lipophilicity on transscleral retinal delivery of six corticosteroids.Drug Metab Dispos. 2011 May;39(5):771-81. doi: 10.1124/dmd.110.037408. Epub 2011 Feb 23. Drug Metab Dispos. 2011. PMID: 21346004 Free PMC article.
-
Permeability of retinal pigment epithelium: effects of permeant molecular weight and lipophilicity.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2005 Feb;46(2):641-6. doi: 10.1167/iovs.04-1051. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2005. PMID: 15671294
-
Effect of eye pigmentation on transscleral drug delivery.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2008 Jan;49(1):333-41. doi: 10.1167/iovs.07-0214. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2008. PMID: 18172110 Free PMC article.
-
Purines in the eye: recent evidence for the physiological and pathological role of purines in the RPE, retinal neurons, astrocytes, Müller cells, lens, trabecular meshwork, cornea and lacrimal gland.Exp Eye Res. 2014 Oct;127:270-9. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2014.08.009. Epub 2014 Aug 20. Exp Eye Res. 2014. PMID: 25151301 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transscleral drug delivery to the posterior eye: prospects of pharmacokinetic modeling.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2006 Nov 15;58(11):1164-81. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2006.07.025. Epub 2006 Sep 16. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2006. PMID: 17069929 Review.
Cited by
-
Hypoxia alters ocular drug transporter expression and activity in rat and calf models: implications for drug delivery.Mol Pharm. 2013 Jun 3;10(6):2350-61. doi: 10.1021/mp3007133. Epub 2013 May 22. Mol Pharm. 2013. Retraction in: Mol Pharm. 2015 Jul 6;12(7):2559. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.5b00367. PMID: 23607566 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
RETRACTED: Influence of choroidal neovascularization and biodegradable polymeric particle size on transscleral sustained delivery of triamcinolone acetonide.Int J Pharm. 2012 Sep 15;434(1-2):140-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2012.05.025. Epub 2012 May 23. Int J Pharm. 2012. PMID: 22633904 Free PMC article.
-
Intravitreal Poly(L-lactide) Microparticles Sustain Retinal and Choroidal Delivery of TG-0054, a Hydrophilic Drug Intended for Neovascular Diseases.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2011 Feb;1(1):76-90. doi: 10.1007/s13346-010-0009-8. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2011. PMID: 22888471 Free PMC article.
-
Lipophilicity and transporter influence on blood-retinal barrier permeability: a comparison with blood-brain barrier permeability.Pharm Res. 2010 Dec;27(12):2715-24. doi: 10.1007/s11095-010-0272-x. Epub 2010 Sep 22. Pharm Res. 2010. PMID: 20859661
-
Hollow Microcapsules as Periocular Drug Depot for Sustained Release of Anti-VEGF Protein.Pharmaceutics. 2019 Jul 11;11(7):330. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics11070330. Pharmaceutics. 2019. PMID: 31336771 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abrahamsson T, Boström S, Bräutigam J, Lagerström PO, Regårdh CG, Vauqelin G. (1988) Binding of the beta-blockers timolol and H 216/44 to ocular melanin. Exp Eye Res 47:565–577 - PubMed
-
- Ayalasomayajula SP, Kompella UB. (2004) Retinal delivery of celecoxib is several-fold higher following subconjunctival administration compared to systemic administration. Pharm Res 21:1797–1804 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

