A regulating role of the JAK2 FERM domain in hyperactivation of JAK2(V617F)
- PMID: 19929856
- PMCID: PMC8514084
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20090615
A regulating role of the JAK2 FERM domain in hyperactivation of JAK2(V617F)
Abstract
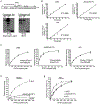
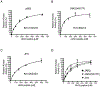
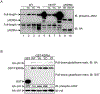
JAK2 (Janus tyrosine kinase 2) is important for signalling through many cytokine receptors, and a gain-of-function JAK2 mutation in its pseudokinase domain, V617F, has been implicated in Philadelphia chromosome-negative myeloproliferative neoplasms. How this mutation hyperactivates JAK2 is poorly understood. In the present paper we report our findings that the V617F mutation has little effect on the Vmax of JAK2 kinase activity, but lowers the Km value for substrates. Therefore under physiological conditions where the concentration level of substrates is presumably below saturation, JAK2(V617F) exhibits hyperactivation compared with wild-type JAK2. This lower Km of JAK2(V617F) towards substrates requires the JAK2 FERM (4.1/ezrin/radixin/moesin) domain, as deletion of the FERM domain abolished this effect. We also show that, in contrast with its positive role in JAK2(V617F) hyperactivation, the FERM domain in wild-type JAK2 is inhibitory. Deletion or mutations of the FERM domain resulted in increased basal JAK2 kinase activity. The results of the present study provide the biochemical basis for how V617F hyperactivates JAK2, and identifies novel regulating roles of the JAK2 FERM domain to control kinase activity at different activation states.
Figures

References
-
- Levine RL, Pardanani A, Tefferi A and Gilliland DG (2007) Role of JAK2 in the pathogenesis and therapy of myeloproliferative disorders. Nat. Rev. Cancer 7, 673–683 - PubMed
-
- Haan C, Kreis S, Margue C and Behrmann I (2006) Jaks and cytokine receptors: an intimate relationship. Biochem. Pharmacol 72, 1538–1546 - PubMed
-
- Huang LJ, Constantinescu SN and Lodish HF (2001) The N-terminal domain of Janus kinase 2 is required for Golgi processing and cell surface expression of erythropoietin receptor. Mol. Cell 8, 1327–1338 - PubMed
-
- Tong W, Sulahian R, Gross AW, Hendon N, Lodish HF and Huang LJ (2006) The membrane-proximal region of the thrombopoietin receptor confers its high surface expression by JAK2-dependent and -independent mechanisms. J. Biol. Chem 281, 38930–38940 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

