Characterisation of microRNA expression in post-natal mouse mammary gland development
- PMID: 19930549
- PMCID: PMC2784809
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-10-548
Characterisation of microRNA expression in post-natal mouse mammary gland development
Abstract
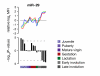
Background: The differential expression pattern of microRNAs (miRNAs) during mammary gland development might provide insights into their role in regulating the homeostasis of the mammary epithelium. Our aim was to analyse these regulatory functions by deriving a comprehensive tissue-specific combined miRNA and mRNA expression profile of post-natal mouse mammary gland development.We measured the expression of 318 individual murine miRNAs by bead-based flow-cytometric profiling of whole mouse mammary glands throughout a 16-point developmental time course, including juvenile, puberty, mature virgin, gestation, lactation, and involution stages. In parallel whole-genome mRNA expression data were obtained.
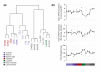
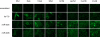
Results: One third (n = 102) of all murine miRNAs analysed were detected during mammary gland development. MicroRNAs were represented in seven temporally co-expressed clusters, which were enriched for both miRNAs belonging to the same family and breast cancer-associated miRNAs. Global miRNA and mRNA expression was significantly reduced during lactation and the early stages of involution after weaning. For most detected miRNA families we did not observe systematic changes in the expression of predicted targets. For miRNA families whose targets did show changes, we observed inverse patterns of miRNA and target expression. The data sets are made publicly available and the combined expression profiles represent an important community resource for mammary gland biology research.
Conclusion: MicroRNAs were expressed in likely co-regulated clusters during mammary gland development. Breast cancer-associated miRNAs were significantly enriched in these clusters. The mechanism and functional consequences of this miRNA co-regulation provide new avenues for research into mammary gland biology and generate candidates for functional validation.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Hormonal regulation of miRNA during mammary gland development.Biol Open. 2024 Jun 15;13(6):bio060308. doi: 10.1242/bio.060308. Epub 2024 Jun 10. Biol Open. 2024. PMID: 38712984 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of microRNA profiles in the mammary gland tissue of dairy goats at the late lactation, dry period and late gestation stages.PLoS One. 2020 Jun 8;15(6):e0234427. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0234427. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32511270 Free PMC article.
-
[microRNA expression in breast development and breast cancer].Pathologe. 2013 Nov;34 Suppl 2:195-200. doi: 10.1007/s00292-013-1878-7. Pathologe. 2013. PMID: 24196612 Review. German.
-
Identification of differentially expressed microRNAs during the development of Chinese murine mammary gland.J Genet Genomics. 2007 Nov;34(11):966-73. doi: 10.1016/S1673-8527(07)60109-X. J Genet Genomics. 2007. PMID: 18037133
-
A mouse mammary gland involution mRNA signature identifies biological pathways potentially associated with breast cancer metastasis.J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2009 Jun;14(2):99-116. doi: 10.1007/s10911-009-9120-1. Epub 2009 Apr 30. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2009. PMID: 19408105 Review.
Cited by
-
miR-205-5p-mediated downregulation of ErbB/HER receptors in breast cancer stem cells results in targeted therapy resistance.Cell Death Dis. 2015 Jul 16;6(7):e1823. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2015.192. Cell Death Dis. 2015. PMID: 26181203 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of the adolescent female breast transcriptome and the impact of obesity.Breast Cancer Res. 2020 May 11;22(1):44. doi: 10.1186/s13058-020-01279-6. Breast Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 32393308 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of microRNA-Associated-ceRNA Networks Regulating Crop Milk Production in Pigeon (Columba livia).Genes (Basel). 2020 Dec 30;12(1):39. doi: 10.3390/genes12010039. Genes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33396684 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA expression profiling identifies decreased expression of miR-205 in inflammatory breast cancer.Mod Pathol. 2016 Apr;29(4):330-46. doi: 10.1038/modpathol.2016.38. Epub 2016 Feb 26. Mod Pathol. 2016. PMID: 26916073 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of miR-30b in the developing mouse mammary gland causes a lactation defect and delays involution.PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e45727. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0045727. Epub 2012 Sep 24. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23029204 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alvarez-Garcia I, Miska EA. MicroRNA functions in animal development and human disease. Development (Cambridge, England) 2005;132(21):4653–4662. - PubMed
-
- Filipowicz W, Bhattacharyya SN, Sonenberg N. Mechanisms of post-transcriptional regulation by microRNAs: are the answers in sight? Nature Reviews. 2008;9(2):102–114. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

