Induction of granzyme B expression in T-cell receptor/CD28-stimulated human regulatory T cells is suppressed by inhibitors of the PI3K-mTOR pathway
- PMID: 19930596
- PMCID: PMC2784757
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2172-10-59
Induction of granzyme B expression in T-cell receptor/CD28-stimulated human regulatory T cells is suppressed by inhibitors of the PI3K-mTOR pathway
Abstract
Background: Regulatory T cells (Tregs) can employ a cell contact- and granzyme B-dependent mechanism to mediate suppression of bystander T and B cells. Murine studies indicate that granzyme B is involved in the Treg-mediated suppression of anti-tumor immunity in the tumor microenvironment and in the Treg-mediated maintenance of allograft survival. In spite of its central importance, a detailed study of granzyme B expression patterns in human Tregs has not been performed.
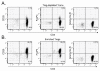
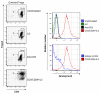
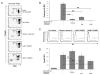
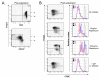
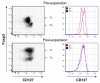
Results: Our data demonstrated that natural Tregs freshly isolated from the peripheral blood of normal adults lacked granzyme B expression. Tregs subjected to prolonged TCR and CD28 triggering, in the presence of IL-2, expressed high levels of granzyme B but CD3 stimulation alone or IL-2 treatment alone failed to induce granzyme B. Treatment of Tregs with the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) inhibitor, rapamycin or the PI3 kinase (PI3K) inhibitor LY294002 markedly suppressed granzyme B expression. However, neither rapamycin, as previously reported by others, nor LY294002 inhibited Treg proliferation or induced significant cell death in TCR/CD28/IL-2 stimulated cells. The proliferation rate of Tregs was markedly higher than that of CD4+ conventional T cells in the setting of rapamycin treatment. Tregs expanded by CD3/CD28/IL-2 stimulation without rapamycin demonstrated increased in vitro cytotoxic activity compared to Tregs expanded in the presence of rapamycin in both short term (6 hours) and long term (48 hours) cytotoxicity assays.
Conclusion: TCR/CD28 mediated activation of the PI3K-mTOR pathway is important for granyzme B expression but not proliferation in regulatory T cells. These findings may indicate that suppressive mechanisms other than granzyme B are utilized by rapamycin-expanded Tregs.
Figures

References
-
- Gondek DC, Lu LF, Quezada SA, Sakaguchi S, Noelle RJ. Cutting edge: contact-mediated suppression by CD4+CD25+ regulatory cells involves a granzyme B-dependent, perforin-independent mechanism. J Immunol. 2005;174:1783–6. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

