Differential requirement for MEK Partner 1 in DU145 prostate cancer cell migration
- PMID: 19930650
- PMCID: PMC2788567
- DOI: 10.1186/1478-811X-7-26
Differential requirement for MEK Partner 1 in DU145 prostate cancer cell migration
Abstract
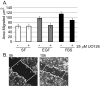
ERK signaling regulates focal adhesion disassembly during cell movement, and increased ERK signaling frequently contributes to enhanced motility of human tumor cells. We previously found that the ERK scaffold MEK Partner 1 (MP1) is required for focal adhesion disassembly in fibroblasts. Here we test the hypothesis that MP1-dependent ERK signaling regulates motility of DU145 prostate cancer cells. We find that MP1 is required for motility on fibronectin, but not for motility stimulated by serum or EGF. Surprisingly, MP1 appears not to function through its known binding partners MEK1 or PAK1, suggesting the existence of a novel pathway by which MP1 can regulate motility on fibronectin. MP1 may function by regulating the stability or expression of paxillin, a key regulator of motility.
Figures



References
-
- American Cancer Society. Cancer Facts and Figures 2008. Atlanta: American Cancer Society; 2008.
-
- Bakin RE, Gioeli D, Sikes RA, Bissonette EA, Weber MJ. Constitutive activation of the Ras/mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway promotes androgen hypersensitivity in LNCaP prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2003;63:1981–1989. - PubMed
-
- Burger M, Denzinger S, Hammerschmied C, Tannapfel A, Maderstorfer A, Wieland WF, Hartmann A, Stoehr R. Mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling is activated in prostate tumors but not mediated by B-RAF mutations. Eur Urol. 2006;50:1102–1109. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2005.11.031. discussion 1109-1110. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

