Osteoinductive LIM mineralization protein-1 suppresses activation of NF-kappaB and selectively regulates MAPK pathways in pre-osteoclasts
- PMID: 19931434
- PMCID: PMC2854312
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bone.2009.11.017
Osteoinductive LIM mineralization protein-1 suppresses activation of NF-kappaB and selectively regulates MAPK pathways in pre-osteoclasts
Abstract
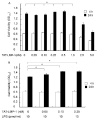
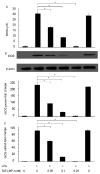
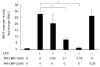
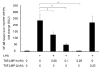
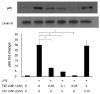
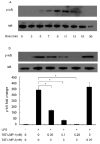
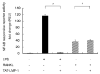
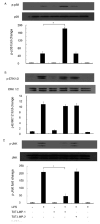
LIM mineralization protein-1 (LMP-1) is an intracellular regulator of bone formation and has been shown to be osteoinductive in vitro and in vivo. The effect of LMP-1 on other aspects of bone homeostasis has not been previously studied. In a pilot study we observed that LMP-1 decreased nitric oxide (NO) production in pre-osteoclasts. Here we report a new anti-inflammatory effect of LMP-1 and define its mechanism of action in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated RAW 264.7 pre-osteoclasts. We found that LMP-1 significantly inhibited LPS-induced NO production. LMP-1 also effectively inhibited the expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), potently suppressed the transcriptional activity and nuclear translocation of nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kappaB), and prevented the phosphorylation of inhibitor of kappa B (IkappaB). Interestingly, LMP-1 had no effect on Receptor-Activator of Nuclear Factor B Ligand (RANKL)-induced activation of NF-kappaB. Furthermore, LMP-1 had no effect on the LPS-induced phosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2), whereas it did attenuate the phosphorylation of c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase (JNK) while enhancing phosphorylation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinases (p38 MAPK). These results suggest that LMP-1 has an anti-inflammatory effect, and this effect is, at least in part, due to the inhibition of NO production by the suppression of NF-kappaB activation and selective regulation of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathways.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sargaquinoic acid isolated from Sargassum siliquastrum inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced nitric oxide production in macrophages via modulation of nuclear factor-κB and c-Jun N-terminal kinase pathways.Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2013 Feb;35(1):80-7. doi: 10.3109/08923973.2012.698622. Epub 2012 Jul 3. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2013. PMID: 22758221
-
Puerarin suppresses production of nitric oxide and inducible nitric oxide synthase in lipopolysaccharide-induced N9 microglial cells through regulating MAPK phosphorylation, O-GlcNAcylation and NF-κB translocation.Int J Oncol. 2012 May;40(5):1610-8. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2012.1331. Epub 2012 Jan 13. Int J Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22246431
-
Methyl-1-hydroxy-2-naphthoate, a novel naphthol derivative, inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response in macrophages via suppression of NF-κB, JNK and p38 MAPK pathways.Inflamm Res. 2011 Sep;60(9):851-9. doi: 10.1007/s00011-011-0345-2. Epub 2011 Jun 11. Inflamm Res. 2011. PMID: 21667204
-
Isoliquiritigenin isolated from the roots of Glycyrrhiza uralensis inhibits LPS-induced iNOS and COX-2 expression via the attenuation of NF-kappaB in RAW 264.7 macrophages.Eur J Pharmacol. 2008 Apr 14;584(1):175-84. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2008.01.032. Epub 2008 Feb 5. Eur J Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18295200
-
Gadd45 proteins as critical signal transducers linking NF-kappaB to MAPK cascades.Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2009 Dec;9(8):915-30. doi: 10.2174/156800909790192383. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2009. PMID: 20025601 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Natural products can modulate inflammation in intervertebral disc degeneration.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Feb 16;14:1150835. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1150835. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36874009 Free PMC article. Review.
-
LIM mineralization protein-1 inhibits IL-1β-induced human chondrocytes injury by altering the NF-κB and MAPK/JNK pathways.Exp Ther Med. 2022 Jan;23(1):61. doi: 10.3892/etm.2021.10983. Epub 2021 Nov 21. Exp Ther Med. 2022. PMID: 34934432 Free PMC article.
-
LIM mineralization protein-1 inhibits the malignant phenotypes of human osteosarcoma cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2014 Apr 23;15(4):7037-48. doi: 10.3390/ijms15047037. Int J Mol Sci. 2014. PMID: 24762763 Free PMC article.
-
Salt-inducible kinase induces cytoplasmic histone deacetylase 4 to promote vascular calcification.EMBO Rep. 2017 Jul;18(7):1166-1185. doi: 10.15252/embr.201643686. Epub 2017 Jun 6. EMBO Rep. 2017. PMID: 28588072 Free PMC article.
-
LIM Mineralization Protein-1 Enhances the Committed Differentiation of Dental Pulp Stem Cells through the ERK1/2 and p38 MAPK Pathways and BMP Signaling.Int J Med Sci. 2022 Jul 18;19(8):1307-1319. doi: 10.7150/ijms.70411. eCollection 2022. Int J Med Sci. 2022. PMID: 35928717 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boden SD, Liu Y, Hair GA, Helms JA, Hu D, Racine M, Nanes MS, Titus L. LMP-1, a LIM-domain protein, mediates BMP-6 effects on bone formation. Endocrinology. 1998;139:5125–34. - PubMed
-
- Boden SD, Titus L, Hair G, Liu Y, Viggeswarapu M, Nanes MS, Baranowski C. Lumbar spine fusion by local gene therapy with a cDNA encoding a novel osteoinductive protein (LMP-1) Spine. 1998;23:2486–92. - PubMed
-
- Viggeswarapu M, Boden SD, Liu Y, Hair GA, Louis-Ugbo J, Murakami H, Kim HS, Mayr MT, Hutton WC, Titus L. Adenoviral delivery of LIM mineralization protein-1 induces new-bone formation in vitro and in vivo. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2001;83-A:364–76. - PubMed
-
- Liu Y, Hair GA, Boden SD, Viggeswarapu M, Titus L. Overexpressed LIM mineralization proteins do not require LIM domains to induce bone. J Bone Miner Res. 2002;17:406–14. - PubMed
-
- Minamide A, Boden SD, Viggeswarapu M, Hair GA, Oliver C, Titus L. Mechanism of bone formation with gene transfer of the cDNA encoding for the intracellular protein LMP-1. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003;85-A:1030–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

