Yohimbine stress potentiates conditioned cue-induced reinstatement of heroin-seeking in rats
- PMID: 19931573
- PMCID: PMC2821948
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbr.2009.11.030
Yohimbine stress potentiates conditioned cue-induced reinstatement of heroin-seeking in rats
Abstract
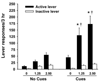
Stress and drug-associated cues can trigger craving and relapse in abstinent drug-dependent individuals. Although the role of these two critical factors in relapse has been extensively studied, the interaction between stress and drug-associated cues in relapse has been less well characterized. Using an animal model of relapse, we assessed the effects of the pharmacological stressor, yohimbine (1.25 or 2.5mg/kg), on reinstatement of extinguished heroin-seeking in rats either in the presence or absence of heroin-associated cues. Yohimbine, in the absence of heroin-associated cues, and cues by themselves reliably reinstated heroin-seeking over extinction levels. Notably, animals showed significantly potentiated responding when yohimbine preceded cue-induced reinstatement (3-4x higher over cues or yohimbine alone). These results demonstrate that exposure to heroin-paired cues during yohimbine-induced stress greatly potentiates heroin-seeking, and support the simultaneous targeting of both stress and cue activation during relapse intervention.
Copyright 2009 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Brooner RK, King VL, Kidorf M, Schmidt CW, Jr., Bigelow GE. Psychiatric and substance use comorbidity among treatment-seeking opioid abusers. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1997;54:71–80. - PubMed
-
- Frances RJ, Miller SI. Clinical Textbook of Addictive Disorders. New York: Guilford Press; 1998.
-
- Blanco C, Alderson D, Ogburn E, Grant BF, Nunes EV, Hatzenbuehler ML, Hasin DS. Changes in the prevalence of non-medical prescription drug use and drug use disorders in the United States: 1991–1992 and 2001–2002. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2007;90:252–260. - PubMed
-
- Compton WM, Volkow ND. Major increases in opioid analgesic abuse in the United States: concerns and strategies. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2006;81:103–107. - PubMed
-
- Gossop M, Stewart D, Browne N, Marsden J. Factors associated with abstinence, lapse or relapse to heroin use after residential treatment: protective effect of coping responses. Addiction. 2002;97:1259–1267. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

