What are the outcomes of radical prostatectomy for high-risk prostate cancer?
- PMID: 19931898
- PMCID: PMC2889156
- DOI: 10.1016/j.urology.2009.09.014
What are the outcomes of radical prostatectomy for high-risk prostate cancer?
Abstract
Objectives: To examine the long-term survival following radical prostatectomy in the population with high-risk prostate cancer. Despite considerable stage migration associated with widespread prostate-specific antigen screening, as many as one-third of incident prostate cancers have high-risk features. These patients are often treated with combined radiation and androgen deprivation therapy, and less is known about the long-term survival in this population after radical prostatectomy (RP).
Methods: Between 1992 and 2008, 175 men underwent RP by a single surgeon with D'Amico high-risk prostate cancer (clinical stage ≥T2c, biopsy Gleason score 8-10, or prostate-specific antigen >20 ng/mL). In this population, we examined the rates and predictors of biochemical progression, metastatic disease, and cancer-specific mortality.
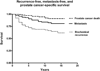
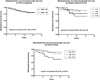
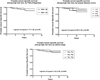
Results: Among 175 high-risk patients, 63 (36%) had organ-confined disease in the RP specimen. At 10 years, biochemical recurrence-free survival was 68%, metastasis-free survival was 84%, and prostate cancer-specific survival was 92%. The 10-year rate of freedom from any hormonal therapy was 71%. Of the high-risk criteria, a biopsy Gleason score of 8-10 (vs ≤7) was the strongest independent predictor of biochemical recurrence, metastases, and prostate cancer death.
Conclusions: National data suggest that RP may be underutilized for the management of high-risk clinically localized prostate cancer. Our data suggest that surgical treatment can result in long-term progression-free survival in a subset of carefully selected high-risk men. Further prospective studies are warranted to directly compare the outcomes of RP vs combined radiation and hormonal therapy in high-risk patients.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- D'Amico AV, Whittington R, Malkowicz SB, et al. Biochemical outcome after radical prostatectomy, external beam radiation therapy, or interstitial radiation therapy for clinically localized prostate cancer. Jama. 1998;280:969–974. - PubMed
-
- Nguyen CT, Reuther AM, Stephenson AJ, et al. The specific definition of high risk prostate cancer has minimal impact on biochemical relapse-free survival. J Urol. 2009;181:75–80. - PubMed
-
- Thompson I, Thrasher JB, Aus G, et al. Guideline for the management of clinically localized prostate cancer: 2007 update. J Urol. 2007;177:2106–2131. - PubMed
-
- Meng MV, Elkin EP, Latini DM, et al. Treatment of patients with high risk localized prostate cancer: results from cancer of the prostate strategic urological research endeavor (CaPSURE) J Urol. 2005;173:1557–1561. - PubMed
-
- Denberg TD, Glode LM, Steiner JF, et al. Trends and predictors of aggressive therapy for clinical locally advanced prostate carcinoma. BJU Int. 2006;98:335–340. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

