Cerebral blood flow characteristics and biometry in fetuses undergoing prenatal intervention for aortic stenosis with evolving hypoplastic left heart syndrome
- PMID: 19931971
- PMCID: PMC4230573
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2009.09.004
Cerebral blood flow characteristics and biometry in fetuses undergoing prenatal intervention for aortic stenosis with evolving hypoplastic left heart syndrome
Abstract
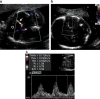
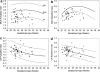
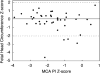
Children with hypoplastic left heart syndrome (HLHS) are at risk for neurodevelopmental dysfunction; prenatal factors may play a role in this predilection. Cerebral blood flow profiles are abnormal in fetuses with HLHS, raising the possibility that cerebral hemodynamics in utero may be related to neurodevelopmental abnormalities. Prenatal aortic valvuloplasty for fetal aortic stenosis with evolving HLHS is technically feasible and improves left heart hemodynamics. This study aimed to assess the effects of prenatal intervention on cerebral blood flow profiles and head circumference in fetuses with evolving HLHS. Seventy fetuses underwent prenatal aortic valvuloplasty for evolving HLHS (median 23 weeks gestation). Among 46 fetuses that had successful valvuloplasty and available data, middle cerebral artery (MCA) pulsatility (PI) and resistive (RI) indices were abnormal (Z-scores -1.7+/-1.1 and -2.2+/-1.4, p<0.001). Early post-valvuloplasty (n=33) and at late gestation follow-up (n=28), MCA PI and RI Z-scores remained low with no difference from pre- or early postintervention. Fetal head circumference was normal, as were umbilical artery PI and RI Z-scores. Cerebral blood flow characteristics are abnormal in mid-gestation fetuses with evolving HLHS, suggesting low cerebral vascular impedance. The mechanisms and significance of these abnormalities are unknown. Prenatal aortic valvuloplasty did not have a major impact on these indices. (E-mail: doff.mcelhinney@cardio.chboston.org).
Figures


Similar articles
-
Tissue Doppler imaging in fetuses with aortic stenosis and evolving hypoplastic left heart syndrome before and after fetal aortic valvuloplasty.Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2016 May;47(5):608-15. doi: 10.1002/uog.14885. Epub 2016 Apr 17. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2016. PMID: 25914144
-
Changes in left heart hemodynamics after technically successful in-utero aortic valvuloplasty.Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2007 Oct;30(5):715-20. doi: 10.1002/uog.5132. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2007. PMID: 17764106
-
Near-Term Cerebroplacental Doppler, Heart Morphology, and Neonatal Biometry in Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome.J Ultrasound Med. 2022 Aug;41(8):2087-2096. doi: 10.1002/jum.15893. Epub 2021 Nov 29. J Ultrasound Med. 2022. PMID: 34842288
-
Fetal cardiac interventions: Where do we stand?Arch Cardiovasc Dis. 2020 Feb;113(2):121-128. doi: 10.1016/j.acvd.2019.06.007. Epub 2020 Feb 26. Arch Cardiovasc Dis. 2020. PMID: 32113817 Review.
-
The outcomes of fetal aortic valvuloplasty in critical aortic stenosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Int J Cardiol. 2023 Jul 1;382:106-111. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2023.03.050. Epub 2023 Mar 29. Int J Cardiol. 2023. PMID: 36996909
Cited by
-
Umbilical artery systolic to diastolic ratio is associated with growth and myocardial performance in infants with hypoplastic left heart syndrome.Prenat Diagn. 2014 Feb;34(2):128-33. doi: 10.1002/pd.4268. Epub 2013 Nov 28. Prenat Diagn. 2014. PMID: 24190763 Free PMC article.
-
Current status of fetal cardiac intervention.Circulation. 2010 Mar 16;121(10):1256-63. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.109.870246. Circulation. 2010. PMID: 20231543 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Abnormal abdominal aorta hemodynamics are associated with necrotizing enterocolitis in infants with hypoplastic left heart syndrome.Pediatr Cardiol. 2014 Apr;35(4):616-21. doi: 10.1007/s00246-013-0828-8. Epub 2013 Oct 24. Pediatr Cardiol. 2014. PMID: 24154504 Free PMC article.
-
New approaches to neuroprotection in infant heart surgery.Pediatr Res. 2010 Jul;68(1):1-9. doi: 10.1203/PDR.0b013e3181df5402. Pediatr Res. 2010. PMID: 20351657 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reversible ductus arteriosus constriction due to maternal indomethacin after fetal intervention for hypoplastic left heart syndrome with intact/restrictive atrial septum.Fetal Diagn Ther. 2010;27(1):40-5. doi: 10.1159/000268290. Epub 2009 Dec 17. Fetal Diagn Ther. 2010. PMID: 20016136 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arduini D, Rizzo G. Normal values of pulsatility index from fetal vessels: A cross-sectional study on 1556 healthy fetuses. J Perinat Med. 1990;18:165–172. - PubMed
-
- Ashwal S, Majcher JS, Vain N, Longo LD. Patterns of fetal lamb regional cerebral blood flow during and after prolonged hypoxia. Pediatr Res. 1980;14:1104–1110. - PubMed
-
- Chihara H, Blood AB, Hunter CJ, Power GG. Effect of mild hypothermia and hypoxia on blood flow and oxygen consumption of the fetal sheep brain. Pediatr Res. 2003;54:665–671. - PubMed
-
- Donofrio MT, Bremer YA, Schieken RM, Gennings C, Morton LD, Eidem BW, Cetta F, Falkensammer CB, Huhta JC, Kleinman CS. Autoregulation of cerebral blood flow in fetuses with congenital heart disease: The brain sparing effect. Pediatr Cardiol. 2003;24:436–443. - PubMed
-
- Doubilet PM, Benson CB, Nadel AS, Ringer SA. Improved birth weight table for neonates developed from gestations dated by early ultrasonography. J Ultrasound Med. 1997;16:241–249. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

