The T box mechanism: tRNA as a regulatory molecule
- PMID: 19932103
- PMCID: PMC2794906
- DOI: 10.1016/j.febslet.2009.11.056
The T box mechanism: tRNA as a regulatory molecule
Abstract
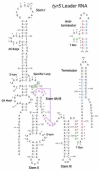
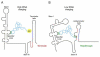
The T box mechanism is widely used in Gram-positive bacteria to regulate expression of aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase genes and genes involved in amino acid biosynthesis and uptake. Binding of a specific uncharged tRNA to a riboswitch element in the nascent transcript causes a structural change in the transcript that promotes expression of the downstream coding sequence. In most cases, this occurs by stabilization of an antiterminator element that competes with formation of a terminator helix. Specific tRNA recognition by the nascent transcript results in increased expression of genes important for tRNA aminoacylation in response to decreased pools of charged tRNA.
Figures
References
-
- Henkin TM. Regulation of aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase gene expression in bacteria. In: Ibba M, Francklyn C, Cusack S, editors. The aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases. Landes Bioscience; 2004. pp. 309–13.
-
- Henkin TM, Grundy FJ. Sensing metabolic signals with nascent RNA transcripts: The T box and S box riboswitches as paradigms. Cold Spring Harbor Symp. Quant. Biol. 2006;71:231–7. - PubMed
-
- Henkin TM, Yanofsky C. Regulation by transcription attenuation in bacteria: how RNA provides instructions for transcription termination/antitermination decisions. BioEssays. 2002;24:700–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

