Protein-precursor tRNA contact leads to sequence-specific recognition of 5' leaders by bacterial ribonuclease P
- PMID: 19932118
- PMCID: PMC2829246
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmb.2009.11.039
Protein-precursor tRNA contact leads to sequence-specific recognition of 5' leaders by bacterial ribonuclease P
Abstract
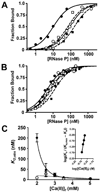
Bacterial ribonuclease P (RNase P) catalyzes the cleavage of 5' leader sequences from precursor tRNAs (pre-tRNAs). Previously, all known substrate nucleotide specificities in this system are derived from RNA-RNA interactions with the RNase P RNA subunit. Here, we demonstrate that pre-tRNA binding affinities for Bacillus subtilis and Escherichia coli RNase P are enhanced by sequence-specific contacts between the fourth pre-tRNA nucleotide on the 5' side of the cleavage site (N(-4)) and the RNase P protein (P protein) subunit. B. subtilis RNase P has a higher affinity for pre-tRNA with adenosine at N(-4), and this binding preference is amplified at physiological divalent ion concentrations. Measurements of pre-tRNA-containing adenosine analogs at N(-4) indicate that specificity arises from a combination of hydrogen bonding to the N6 exocyclic amine of adenosine and steric exclusion of the N2 amine of guanosine. Mutagenesis of B. subtilis P protein indicates that F20 and Y34 contribute to selectivity at N(-4). The hydroxyl group of Y34 enhances selectivity, likely by forming a hydrogen bond with the N(-4) nucleotide. The sequence preference of E. coli RNase P is diminished, showing a weak preference for adenosine and cytosine at N(-4), consistent with the substitution of Leu for Y34 in the E. coli P protein. This is the first identification of a sequence-specific contact between P protein and pre-tRNA that contributes to molecular recognition of RNase P. Additionally, sequence analyses reveal that a greater-than-expected fraction of pre-tRNAs from both E. coli and B. subtilis contains a nucleotide at N(-4) that enhances RNase P affinity. This observation suggests that specificity at N(-4) contributes to substrate recognition in vivo. Furthermore, bioinformatic analyses suggest that sequence-specific contacts between the protein subunit and the leader sequences of pre-tRNAs may be common in bacterial RNase P and may lead to species-specific substrate recognition.
Copyright 2009 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The RNR motif of B. subtilis RNase P protein interacts with both PRNA and pre-tRNA to stabilize an active conformer.RNA. 2011 Jul;17(7):1225-35. doi: 10.1261/rna.2742511. Epub 2011 May 27. RNA. 2011. PMID: 21622899 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of individual nucleotides in the bacterial ribonuclease P ribozyme adjacent to the pre-tRNA cleavage site by short-range photo-cross-linking.Biochemistry. 1998 Dec 15;37(50):17618-28. doi: 10.1021/bi982050a. Biochemistry. 1998. PMID: 9860878
-
Interaction of the 3'-end of tRNA with ribonuclease P RNA.Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Oct 11;22(20):4087-94. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.20.4087. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994. PMID: 7524035 Free PMC article.
-
RNase P from bacteria. Substrate recognition and function of the protein subunit.Mol Biol Rep. 1995-1996;22(2-3):99-109. doi: 10.1007/BF00988713. Mol Biol Rep. 1995. PMID: 8901495 Review.
-
The specificity landscape of bacterial ribonuclease P.J Biol Chem. 2024 Jan;300(1):105498. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2023.105498. Epub 2023 Nov 25. J Biol Chem. 2024. PMID: 38013087 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Analysis of the RNA Binding Specificity Landscape of C5 Protein Reveals Structure and Sequence Preferences that Direct RNase P Specificity.Cell Chem Biol. 2016 Oct 20;23(10):1271-1281. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2016.09.002. Epub 2016 Sep 29. Cell Chem Biol. 2016. PMID: 27693057 Free PMC article.
-
The L7Ae protein binds to two kink-turns in the Pyrococcus furiosus RNase P RNA.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Dec 1;42(21):13328-38. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku994. Epub 2014 Oct 31. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 25361963 Free PMC article.
-
The rph-1-Encoded Truncated RNase PH Protein Inhibits RNase P Maturation of Pre-tRNAs with Short Leader Sequences in the Absence of RppH.J Bacteriol. 2017 Oct 17;199(22):e00301-17. doi: 10.1128/JB.00301-17. Print 2017 Nov 15. J Bacteriol. 2017. PMID: 28808133 Free PMC article.
-
Dissecting functional cooperation among protein subunits in archaeal RNase P, a catalytic ribonucleoprotein complex.Nucleic Acids Res. 2010 Dec;38(22):8316-27. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq668. Epub 2010 Aug 12. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010. PMID: 20705647 Free PMC article.
-
Archaeal/eukaryal RNase P: subunits, functions and RNA diversification.Nucleic Acids Res. 2010 Dec;38(22):7885-94. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq701. Epub 2010 Aug 16. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010. PMID: 20716516 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Smith JK, Hsieh J, Fierke CA. Importance of RNA-protein interactions in bacterial ribonuclease P structure and catalysis. Biopolymers. 2007;87:329–338. - PubMed
-
- Kirsebom LA. RNase P RNA mediated cleavage: substrate recognition and catalysis. Biochimie. 2007;89:1183–1194. - PubMed
-
- Christian EL, Zahler NH, Kaye NM, Harris ME. Analysis of substrate recognition by the ribonucleoprotein endonuclease RNase P. Methods. 2002;28:307–322. - PubMed
-
- Beebe JA, Fierke CA. A kinetic mechanism for cleavage of precursor tRNA(Asp) catalyzed by the RNA component of Bacillus subtilis ribonuclease P. Biochemistry. 1994;33:10294–10304. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

