Memory-enhancing corticosterone treatment increases amygdala norepinephrine and Arc protein expression in hippocampal synaptic fractions
- PMID: 19932757
- PMCID: PMC5639692
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nlm.2009.11.005
Memory-enhancing corticosterone treatment increases amygdala norepinephrine and Arc protein expression in hippocampal synaptic fractions
Abstract
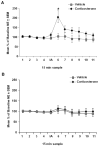
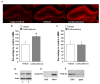
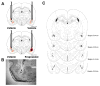
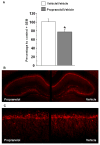
Considerable evidence indicates that glucocorticoid hormones enhance the consolidation of memory for emotionally arousing events through interactions with the noradrenergic system of the basolateral complex of the amygdala (BLA). We previously reported that intra-BLA administration of a beta-adrenoceptor agonist immediately after inhibitory avoidance training enhanced memory consolidation and increased hippocampal expression of the protein product of the immediate early gene activity-regulated cytoskeletal-associated protein (Arc). In the present experiments corticosterone (3 mg/kg, i.p.) was administered to male Sprague-Dawley rats immediately after inhibitory avoidance training to examine effects on long-term memory, amygdala norepinephrine levels, and hippocampal Arc expression. Corticosterone increased amygdala norepinephrine levels 15 min after inhibitory avoidance training, as assessed by in vivo microdialysis, and enhanced memory tested at 48 h. Corticosterone treatment also increased expression of Arc protein in hippocampal synaptic tissue. The elevation in BLA norepinephrine appears to participate in corticosterone-influenced modulation of hippocampal Arc expression as intra-BLA blockade of beta-adrenoceptors with propranolol (0.5 microg/0.2 microL) attenuated the corticosterone-induced synaptic Arc expression in the hippocampus. These findings indicate that noradrenergic activity at BLA beta-adrenoceptors is involved in corticosterone-induced enhancement of memory consolidation and expression of the synaptic-plasticity-related protein Arc in the hippocampus.
2009 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Corticosterone-induced enhancement of memory and synaptic Arc protein in the medial prefrontal cortex.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2014 Jul;112:148-57. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2014.02.007. Epub 2014 Mar 3. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2014. PMID: 24603007 Free PMC article.
-
Post-training intra-basolateral complex of the amygdala infusions of clenbuterol enhance memory for conditioned place preference and increase ARC protein expression in dorsal hippocampal synaptic fractions.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2021 Nov;185:107539. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2021.107539. Epub 2021 Oct 12. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2021. PMID: 34648950 Free PMC article.
-
Noradrenergic actions in the basolateral complex of the amygdala modulate Arc expression in hippocampal synapses and consolidation of aversive and non-aversive memory.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2014 Nov;115:49-57. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2014.08.016. Epub 2014 Sep 6. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2014. PMID: 25196704 Free PMC article.
-
1999 Curt P. Richter award. Glucocorticoids and the regulation of memory consolidation.Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2000 Apr;25(3):213-38. doi: 10.1016/s0306-4530(99)00058-x. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2000. PMID: 10737694 Review.
-
Role of norepinephrine in mediating stress hormone regulation of long-term memory storage: a critical involvement of the amygdala.Biol Psychiatry. 1999 Nov 1;46(9):1140-52. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3223(99)00157-2. Biol Psychiatry. 1999. PMID: 10560021 Review.
Cited by
-
Glucocorticoid-dependent hippocampal transcriptome in male rats: pathway-specific alterations with aging.Endocrinology. 2013 Aug;154(8):2807-20. doi: 10.1210/en.2013-1139. Epub 2013 Jun 4. Endocrinology. 2013. PMID: 23736296 Free PMC article.
-
Memory-enhancing intra-basolateral amygdala infusions of clenbuterol increase Arc and CaMKIIα protein expression in the rostral anterior cingulate cortex.Front Behav Neurosci. 2012 Apr 19;6:17. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2012.00017. eCollection 2012. Front Behav Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22529784 Free PMC article.
-
Glucocorticoid receptors recruit the CaMKIIα-BDNF-CREB pathways to mediate memory consolidation.Nat Neurosci. 2012 Dec;15(12):1707-14. doi: 10.1038/nn.3266. Epub 2012 Nov 18. Nat Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 23160045 Free PMC article.
-
The Neurobiology of Fear Generalization.Front Behav Neurosci. 2019 Jan 15;12:329. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2018.00329. eCollection 2018. Front Behav Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30697153 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of a co-treatment with pyruvate and creatine on dendritic spines in rat hippocampus and posterodorsal medial amygdala in a phenylketonuria animal model.Metab Brain Dis. 2013 Sep;28(3):509-17. doi: 10.1007/s11011-013-9389-z. Epub 2013 Feb 22. Metab Brain Dis. 2013. PMID: 23430365
References
-
- Bloomer WAC, VanDongen HMA, VanDongen AMJ. Arc/Arg3.1 translation is controlled by convergent N-methyl-D-aspartate and Gs-coupled receptor signaling pathways. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2007;283:582–592. - PubMed
-
- Cahill L, Alkire MT. Epinephrine enhancement of human memory consolidation: interaction with arousal at encoding. Neurobiology of Learning and Memory. 2003;79:194–198. - PubMed
-
- de Quervain DJ, Roozendaal B, McGaugh JL. Stress and glucocorticoids impair retrieval of long-term spatial memory. Nature. 1998;394:787–790. - PubMed
-
- Diamond DM, Park CR, Woodson JC. Stress generates emotional memories and retrograde amnesia by inducing an endogenous form of hippocampal LTP. Hippocampus. 2002;14:281–291. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

