Mapping polypeptide interactions of the SecA ATPase during translocation
- PMID: 19933328
- PMCID: PMC2780316
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0910550106
Mapping polypeptide interactions of the SecA ATPase during translocation
Abstract
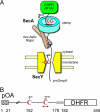
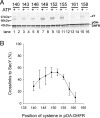
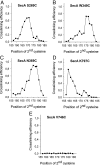
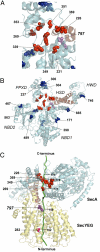
Many bacterial proteins, including most secretory proteins, are translocated across the plasma membrane by the interplay of the cytoplasmic SecA ATPase and a protein-conducting channel formed by the SecY complex. SecA catalyzes the sequential movement of polypeptide segments through the SecY channel. How SecA interacts with a broad range of polypeptide segments is unclear, but structural data raise the possibility that translocation substrates bind into a "clamp" of SecA. Here, we have used disulfide bridge cross-linking to test this hypothesis. To analyze polypeptide interactions of SecA during translocation, two cysteines were introduced into a translocation intermediate: one that cross-links to the SecY channel and the other one for cross-linking to a cysteine placed at various positions in SecA. Our results show that a translocating polypeptide is indeed captured inside SecA's clamp and moves in an extended conformation through the clamp into the SecY channel. These results define the polypeptide path during SecA-mediated protein translocation and suggest a mechanism by which ATP hydrolysis by SecA is used to move a polypeptide chain through the SecY channel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

