Quantitative characterization of low-threshold mechanoreceptor inputs to lamina I spinoparabrachial neurons in the rat
- PMID: 19933757
- PMCID: PMC2821553
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2009.181511
Quantitative characterization of low-threshold mechanoreceptor inputs to lamina I spinoparabrachial neurons in the rat
Abstract
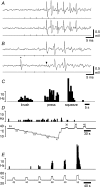
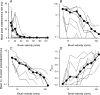
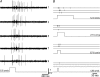
It has been suggested that primary afferent C-fibres that respond to innocuous tactile stimuli are important in the sensation of pleasurable touch. Although it is known that C-tactile fibres terminate in the substantia gelatinosa (lamina II) of the spinal cord, virtually all of the neurons in this region are interneurons, and currently it is not known how impulses in C-mechanoreceptors are transmitted to higher centres. In the current study, I have tested the quantitative response properties of 'wide dynamic range' projection neurons in lamina I of the spinal cord to graded velocity brushing stimuli to identify whether low-threshold mechanoreceptor input to these neurons arises from myelinated or umyelinated nerve fibres. Graded velocity brushing stimuli (6.6-126 cm s(-1)) were used to characterize the mechanoreceptor inputs to 'wide dynamic range' neurons in lamina I of the dorsal horn that had axons that projected to the contralateral parabrachial nucleus. The most effective tactile stimuli for activation of 'wide dynamic range' lamina I spinoparabrachial neurons were low velocity brush strokes: peak discharge occurred at a mean velocity of 9.2 cm s(-1) (range 6.6-20.4 cm s(-1), s.d. 5.0 cm s(-1)), and declined exponentially as brush velocity increased. The data indicate that C-fibres, but not A-fibres, conveyed low-threshold mechanoreceptor inputs to lamina I projection neurons.
Figures

Comment in
-
Why a soft touch can hurt.J Physiol. 2010 Jan 1;588(Pt 1):13. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2009.185116. J Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20045900 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Alden M, Besson JM, Bernard JF. Organization of the efferent projections from the pontine parabrachial area to the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis and neighboring regions: a PHA-L study in the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1994;341:289–314. - PubMed
-
- Bernard JF, Alden M, Besson JM. The organization of the efferent projections from the pontine parabrachial area to the amygdaloid complex: a Phaseolus vulgaris leucoagglutinin (PHA-L) study in the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1993;329:201–229. - PubMed
-
- Bessou P, Burgess PR, Perl ER, Taylor CB. Dynamic properties of mechanoreceptors with unmyelinated (C) fibres. J Neurophysiol. 1971;34:116–131. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

