Voriconazole pharmacokinetics in liver transplant recipients
- PMID: 19933807
- PMCID: PMC2812143
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00429-09
Voriconazole pharmacokinetics in liver transplant recipients
Abstract
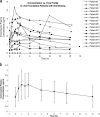
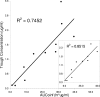
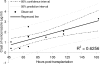
The objective of this study was to evaluate the pharmacokinetics of voriconazole and the potential correlations between pharmacokinetic parameters and patient variables in liver transplant patients on a fixed-dose prophylactic regimen. Multiple blood samples were collected within one dosing interval from 15 patients who were initiated on a prophylactic regimen of voriconazole at 200 mg enterally (tablets) twice daily starting immediately posttransplant. Voriconazole plasma concentrations were measured using high-pressure liquid chromatography (HPLC). Noncompartmental pharmacokinetic analysis was performed to estimate pharmacokinetic parameters. The mean apparent systemic clearance over bioavailability (CL/F), apparent steady-state volume of distribution over bioavailability (Vss/F), and half-life (t1/2) were 5.8+/-5.5 liters/h, 94.5+/-54.9 liters, and 15.7+/-7.0 h, respectively. There was a good correlation between the area under the concentration-time curve from 0 h to infinity (AUC0-infinity) and trough voriconazole plasma concentrations. t1/2, maximum drug concentration in plasma (Cmax), trough level, AUC0-infinity, area under the first moment of the concentration-time curve from 0 h to infinity (AUMC0-infinity), and mean residence time from 0 h to infinity (MRT0-infinity) were significantly correlated with postoperative time. t1/2, lambda, AUC0-infinity, and CL/F were significantly correlated with indices of liver function (aspartate transaminase [AST], total bilirubin, and international normalized ratio [INR]). The Cmax, last concentration in plasma at 12 h (Clast), AUMC0-infinity, and MRT0-infinity were significantly lower in the presence of deficient CYP2C19*2 alleles. Donor characteristics had no significant correlation with any of the pharmacokinetic parameters estimated. A fixed dosing regimen of voriconazole results in a highly variable exposure of voriconazole in liver transplant patients. Given that trough voriconazole concentration is a good measure of drug exposure (AUC), the voriconazole dose can be individualized based on trough concentration measurements in liver transplant patients.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Bioavailability and population pharmacokinetics of voriconazole in lung transplant recipients.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010 Oct;54(10):4424-31. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00504-10. Epub 2010 Aug 2. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010. PMID: 20679503 Free PMC article.
-
Population pharmacokinetic evaluation with external validation and Bayesian estimator of voriconazole in liver transplant recipients.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2011 Mar;50(3):201-14. doi: 10.2165/11538690-000000000-00000. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2011. PMID: 21294597
-
The CYP2C19 ultra-rapid metabolizer genotype influences the pharmacokinetics of voriconazole in healthy male volunteers.Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2009 Mar;65(3):281-5. doi: 10.1007/s00228-008-0574-7. Epub 2008 Nov 4. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 18982321
-
Pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic profile of voriconazole.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2006;45(7):649-63. doi: 10.2165/00003088-200645070-00002. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2006. PMID: 16802848 Review.
-
Treatment of refractory cerebral aspergillosis in a liver transplant recipient with voriconazole: case report and review of the literature.Exp Clin Transplant. 2012 Oct;10(5):482-6. doi: 10.6002/ect.2012.0028. Exp Clin Transplant. 2012. PMID: 23031086 Review.
Cited by
-
Enhancing voriconazole therapy in liver dysfunction: exploring administration schemes and predictive factors for trough concentration and efficacy.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jan 4;14:1323755. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1323755. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38239188 Free PMC article.
-
Voriconazole therapeutic drug monitoring: retrospective cohort study of the relationship to clinical outcomes and adverse events.BMC Infect Dis. 2013 Feb 26;13:105. doi: 10.1186/1471-2334-13-105. BMC Infect Dis. 2013. PMID: 23442261 Free PMC article.
-
Factors influencing voriconazole plasma level in intensive care patients.JAC Antimicrob Resist. 2024 Mar 18;6(2):dlae045. doi: 10.1093/jacamr/dlae045. eCollection 2024 Apr. JAC Antimicrob Resist. 2024. PMID: 38500519 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of cytochrome P450 2C19 genotype on voriconazole exposure in cystic fibrosis lung transplant patients.Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2011 Mar;67(3):253-60. doi: 10.1007/s00228-010-0914-2. Epub 2010 Oct 31. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21038076
-
Impact of Albumin and Omeprazole on Steady-State Population Pharmacokinetics of Voriconazole and Development of a Voriconazole Dosing Optimization Model in Thai Patients with Hematologic Diseases.Antibiotics (Basel). 2020 Sep 3;9(9):574. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics9090574. Antibiotics (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32899425 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boyd, A. E., S. Modi, et al. 2004. Adverse reactions to voriconazole. Clin. Infect. Dis. 39:1241-1244. - PubMed
-
- Capitano, B., B. Potoski, et al. 2004. Pharmacokinetics of voriconazole in lung transplant patients, abstr. A-39. Abstr. 44th Intersci. Conf. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, DC.
-
- Denning, D. W., P. Ribaud, et al. 2002. Efficacy and safety of voriconazole in the treatment of acute invasive aspergillosis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 34:563-571. - PubMed
-
- Desta, Z., X. Zhao, et al. 2002. Clinical significance of the cytochrome P450 2C19 genetic polymorphism. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 41:913-958. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

