Both XPD alleles contribute to the phenotype of compound heterozygote xeroderma pigmentosum patients
- PMID: 19934020
- PMCID: PMC2806454
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20091892
Both XPD alleles contribute to the phenotype of compound heterozygote xeroderma pigmentosum patients
Abstract
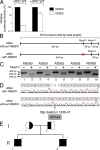
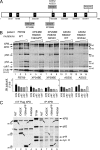
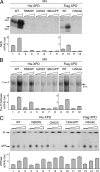
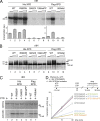
Mutations in the XPD subunit of the DNA repair/transcription factor TFIIH result in the rare recessive genetic disorder xeroderma pigmentosum (XP). Many XP patients are compound heterozygotes with a "causative" XPD point mutation R683W and different second mutant alleles, considered "null alleles." However, there is marked clinical heterogeneity (including presence or absence of skin cancers or neurological degeneration) in these XPD/R683W patients, thus suggesting a contribution of the second allele. Here, we report XP patients carrying XPD/R683W and a second XPD allele either XPD/Q452X, /I455del, or /199insPP. We performed a systematic study of the effect of these XPD mutations on several enzymatic functions of TFIIH and found that each mutation exhibited unique biochemical properties. Although all the mutations inhibited the nucleotide excision repair (NER) by disturbing the XPD helicase function, each of them disrupted specific molecular steps during transcription: XPD/Q452X hindered the transactivation process, XPD/I455del disturbed RNA polymerase II phosphorylation, and XPD/199insPP inhibited kinase activity of the cdk7 subunit of TFIIH. The broad range and severity of clinical features in XP patients arise from a broad set of deficiencies in NER and transcription that result from the combination of mutations found on both XPD alleles.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Abnormal XPD-induced nuclear receptor transactivation in DNA repair disorders: trichothiodystrophy and xeroderma pigmentosum.Eur J Hum Genet. 2013 Aug;21(8):831-7. doi: 10.1038/ejhg.2012.246. Epub 2012 Dec 12. Eur J Hum Genet. 2013. PMID: 23232694 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative study of nucleotide excision repair defects between XPD-mutated fibroblasts derived from trichothiodystrophy and xeroderma pigmentosum patients.DNA Repair (Amst). 2008 Dec 1;7(12):1990-8. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2008.08.009. Epub 2008 Oct 10. DNA Repair (Amst). 2008. PMID: 18817897
-
Effects of compound heterozygosity at the Xpd locus on cancer and ageing in mouse models.DNA Repair (Amst). 2012 Nov 1;11(11):874-83. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2012.08.003. Epub 2012 Oct 7. DNA Repair (Amst). 2012. PMID: 23046824
-
XPB and XPD helicases in TFIIH orchestrate DNA duplex opening and damage verification to coordinate repair with transcription and cell cycle via CAK kinase.DNA Repair (Amst). 2011 Jul 15;10(7):697-713. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2011.04.028. Epub 2011 May 14. DNA Repair (Amst). 2011. PMID: 21571596 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The 14th Datta Lecture. TFIIH: from transcription to clinic.FEBS Lett. 2001 Jun 8;498(2-3):124-8. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(01)02458-9. FEBS Lett. 2001. PMID: 11412842 Review.
Cited by
-
Cytosolic sequestration of the vitamin D receptor as a therapeutic option for vitamin D-induced hypercalcemia.Nat Commun. 2020 Dec 7;11(1):6249. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-20069-4. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 33288743 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription preinitiation complex structure and dynamics provide insight into genetic diseases.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2019 Jun;26(6):397-406. doi: 10.1038/s41594-019-0220-3. Epub 2019 May 20. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 31110295 Free PMC article.
-
Ocular manifestations of trichothiodystrophy.Ophthalmology. 2011 Dec;118(12):2335-42. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2011.05.036. Epub 2011 Sep 28. Ophthalmology. 2011. PMID: 21959366 Free PMC article.
-
Disease-causing missense mutations in human DNA helicase disorders.Mutat Res. 2013 Apr-Jun;752(2):138-152. doi: 10.1016/j.mrrev.2012.12.004. Epub 2012 Dec 28. Mutat Res. 2013. PMID: 23276657 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TFIIH: when transcription met DNA repair.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2012 May 10;13(6):343-54. doi: 10.1038/nrm3350. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22572993 Review.
References
-
- Araújo S.J., Tirode F., Coin F., Pospiech H., Syväoja J.E., Stucki M., Hübscher U., Egly J.M., Wood R.D. 2000. Nucleotide excision repair of DNA with recombinant human proteins: definition of the minimal set of factors, active forms of TFIIH, and modulation by CAK. Genes Dev. 14:349–359 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

