Poly(A)-binding protein modulates mRNA susceptibility to cap-dependent miRNA-mediated repression
- PMID: 19934229
- PMCID: PMC2802033
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.1795410
Poly(A)-binding protein modulates mRNA susceptibility to cap-dependent miRNA-mediated repression
Abstract
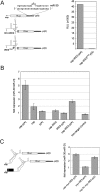
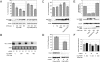
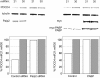
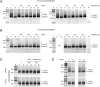
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) regulate gene expression post-transcriptionally through binding specific sites within the 3' untranslated regions (UTRs) of their target mRNAs. Numerous investigations have documented repressive effects of miRNAs and identified factors required for their activity. However, the precise mechanisms by which miRNAs modulate gene expression are still obscure. Here, we have examined the effects of multiple miRNAs on diverse target transcripts containing artificial or naturally occurring 3' UTRs in human cell culture. In agreement with previous studies, we report that both the 5' m(7)G cap and 3' poly(A) tail are essential for maximum miRNA repression. These cis-acting elements also conferred miRNA susceptibility to target mRNAs translating under the control of viral- and eukaryotic mRNA-derived 5' UTR structures that enable cap-independent translation. Additionally, we evaluated a role for the poly(A)-binding protein (PABP) in miRNA function utilizing multiple approaches to modulate levels of active PABP in cells. PABP expression and activity inversely correlated with the strength of miRNA silencing, in part due to antagonism of target mRNA deadenylation. Together, these findings further define the cis- and trans-acting factors that modulate miRNA efficacy.
Figures
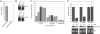
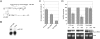
Similar articles
-
Let-7 microRNA-mediated mRNA deadenylation and translational repression in a mammalian cell-free system.Genes Dev. 2007 Aug 1;21(15):1857-62. doi: 10.1101/gad.1566707. Genes Dev. 2007. PMID: 17671087 Free PMC article.
-
Mammalian miRNA RISC recruits CAF1 and PABP to affect PABP-dependent deadenylation.Mol Cell. 2009 Sep 24;35(6):868-80. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2009.08.004. Epub 2009 Aug 27. Mol Cell. 2009. PMID: 19716330 Free PMC article.
-
A Specialized Mechanism of Translation Mediated by FXR1a-Associated MicroRNP in Cellular Quiescence.Mol Cell. 2016 Mar 3;61(5):760-773. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2016.02.013. Mol Cell. 2016. PMID: 26942679 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of poly(A)-binding protein through PABP-interacting proteins.Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2006;71:537-43. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2006.71.061. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2006. PMID: 17381337 Review.
-
Cap and cap-binding proteins in the control of gene expression.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2011 Mar-Apr;2(2):277-98. doi: 10.1002/wrna.52. Epub 2010 Oct 28. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2011. PMID: 21957010 Review.
Cited by
-
p38α mitogen-activated protein kinase depletion and repression of signal transduction to translation machinery by miR-124 and -128 in neurons.Mol Cell Biol. 2013 Jan;33(1):127-35. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00695-12. Epub 2012 Oct 29. Mol Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23109423 Free PMC article.
-
The interactions of GW182 proteins with PABP and deadenylases are required for both translational repression and degradation of miRNA targets.Nucleic Acids Res. 2013 Jan;41(2):978-94. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks1078. Epub 2012 Nov 21. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013. PMID: 23172285 Free PMC article.
-
Attenuation of neurovirulence, biodistribution, and shedding of a poliovirus:rhinovirus chimera after intrathalamic inoculation in Macaca fascicularis.J Virol. 2012 Mar;86(5):2750-9. doi: 10.1128/JVI.06427-11. Epub 2011 Dec 14. J Virol. 2012. PMID: 22171271 Free PMC article.
-
Interplay between polyadenylate-binding protein 1 and Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus ORF57 in accumulation of polyadenylated nuclear RNA, a viral long noncoding RNA.J Virol. 2013 Jan;87(1):243-56. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01693-12. Epub 2012 Oct 17. J Virol. 2013. PMID: 23077296 Free PMC article.
-
ROCK1/MLC2 inhibition induces decay of viral mRNA in BPXV infected cells.Sci Rep. 2022 Oct 24;12(1):17811. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-21610-9. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36280692 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Asangani IA, Rasheed SA, Nikolova DA, Leupold JH, Colburn NH, Post S, Allgayer H. MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) post-transcriptionally downregulates tumor suppressor Pdcd4 and stimulates invasion, intravasation and metastasis in colorectal cancer. Oncogene. 2008;27:2128–2136. - PubMed
-
- Bagga S, Bracht J, Hunter S, Massirer K, Holtz J, Eachus R, Pasquinelli AE. Regulation by let-7 and lin-4 miRNAs results in target mRNA degradation. Cell. 2005;122:553–563. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
