An internal ribosomal entry site mediates redox-sensitive translation of Nrf2
- PMID: 19934254
- PMCID: PMC2817467
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkp1048
An internal ribosomal entry site mediates redox-sensitive translation of Nrf2
Abstract
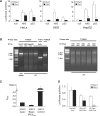
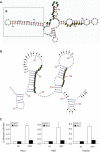
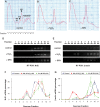
Nrf2 plays pivotal roles in coordinating the antioxidant response and maintaining redox homeostasis. Nrf2 expression is exquisitely regulated; Nrf2 expression is suppressed under unstressed conditions but strikingly induced under oxidative stress. Previous studies showed that stress-induced Nrf2 up-regulation results from both the inhibition of Nrf2 degradation and enhanced Nrf2 translation. In the present study, we elucidate the mechanism underlying translational control of Nrf2. An internal ribosomal entry site (IRES) was identified within the 5' untranslated region of human Nrf2 mRNA. The IRES(Nrf2) contains a highly conserved 18S rRNA binding site (RBS) that is required for internal initiation. This IRES(Nrf2) also contains a hairpin structured inhibitory element (IE) located upstream of the RBS. Deletion of this IE remarkably enhanced translation. Significantly, treatment of cells with hydrogen peroxide (H(2)O(2)) and phyto-oxidant sulforaphane further stimulated IRES(Nrf2)-mediated translation initiation despite the attenuation of global protein synthesis. Polyribosomal profile assay confirmed that endogenous Nrf2 mRNAs were recruited into polysomal fractions under oxidative stress conditions. Collectively, these data demonstrate that Nrf2 translation is suppressed under normal conditions and specifically enhanced upon oxidant exposure by internal initiation, and provide a mechanistic explanation for translational control of Nrf2 by oxidative stress.
Figures



Similar articles
-
La autoantigen mediates oxidant induced de novo Nrf2 protein translation.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2012 Jun;11(6):M111.015032. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M111.015032. Epub 2011 Dec 29. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2012. PMID: 22207702 Free PMC article.
-
Complementarity between the mRNA 5' untranslated region and 18S ribosomal RNA can inhibit translation.RNA. 2000 Apr;6(4):584-97. doi: 10.1017/s1355838200992239. RNA. 2000. PMID: 10786849 Free PMC article.
-
The Triticum Mosaic Virus Internal Ribosome Entry Site Relies on a Picornavirus-Like YX-AUG Motif To Designate the Preferred Translation Initiation Site and To Likely Target the 18S rRNA.J Virol. 2019 Feb 19;93(5):e01705-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01705-18. Print 2019 Mar 1. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 30541835 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatitis C Virus Translation Regulation.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Mar 27;21(7):2328. doi: 10.3390/ijms21072328. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32230899 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Re-programming of translation following cell stress allows IRES-mediated translation to predominate.Biol Cell. 2008 Jan;100(1):27-38. doi: 10.1042/BC20070098. Biol Cell. 2008. PMID: 18072942 Review.
Cited by
-
Amino acid sensing in dietary-restriction-mediated longevity: roles of signal-transducing kinases GCN2 and TOR.Biochem J. 2013 Jan 1;449(1):1-10. doi: 10.1042/BJ20121098. Biochem J. 2013. PMID: 23216249 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reversal of G-Quadruplexes' Role in Translation Control When Present in the Context of an IRES.Biomolecules. 2022 Feb 16;12(2):314. doi: 10.3390/biom12020314. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 35204814 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quantitative proteomic analyses uncover regulatory roles of Nrf2 in human endothelial cells.Cell Stress Chaperones. 2023 Nov;28(6):731-747. doi: 10.1007/s12192-023-01366-5. Epub 2023 Jul 25. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2023. PMID: 37488350 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid Peroxidation and Type I Interferon Coupling Fuels Pathogenic Macrophage Activation Causing Tuberculosis Susceptibility.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 May 1:2024.03.05.583602. doi: 10.1101/2024.03.05.583602. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 38496444 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Nrf2 at the heart of oxidative stress and cardiac protection.Physiol Genomics. 2018 Feb 1;50(2):77-97. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00041.2017. Epub 2017 Nov 29. Physiol Genomics. 2018. PMID: 29187515 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hellen CU, Sarnow P. Internal ribosome entry sites in eukaryotic mRNA molecules. Genes Dev. 2001;15:1593–1612. - PubMed
-
- Stoneley M, Willis AE. Cellular internal ribosome entry segments: structures, trans-acting factors and regulation of gene expression. Oncogene. 2004;23:3200–3207. - PubMed
-
- Holcik M, Sonenberg N. Translational control in stress and apoptosis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2005;6:318–327. - PubMed
-
- Komar AA, Hatzoglou M. Internal ribosome entry sites in cellular mRNAs: mystery of their existence. J. Biol. Chem. 2005;280:23425–23428. - PubMed

