Method comparison of automated matching software-assisted cone-beam CT and stereoscopic kilovoltage x-ray positional verification image-guided radiation therapy for head and neck cancer: a prospective analysis
- PMID: 19934488
- PMCID: PMC5343752
- DOI: 10.1088/0031-9155/54/24/010
Method comparison of automated matching software-assisted cone-beam CT and stereoscopic kilovoltage x-ray positional verification image-guided radiation therapy for head and neck cancer: a prospective analysis
Abstract
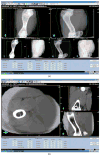
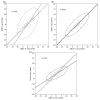
We sought to characterize interchangeability and agreement between cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) and digital stereoscopic kV x-ray (KVX) acquisition, two methods of isocenter positional verification currently used for IGRT of head and neck cancers (HNC). A cohort of 33 patients were near-simultaneously imaged by in-room KVX and CBCT. KVX and CBCT shifts were suggested using manufacturer software for the lateral (X), vertical (Y) and longitudinal (Z) dimensions. Intra-method repeatability, systematic and random error components were calculated for each imaging modality, as were recipe-based PTV expansion margins. Inter-method agreement in each axis was compared using limits of agreement (LOA) methodology, concordance analysis and orthogonal regression. 100 daily positional assessments were performed before daily therapy in 33 patients with head and neck cancer. Systematic error was greater for CBCT in all axes, with larger random error components in the Y- and Z-axis. Repeatability ranged from 9 to 14 mm for all axes, with CBCT showing greater repeatability in 2/3 axes. LOA showed paired shifts to agree 95% of the time within +/-11.3 mm in the X-axis, +/-9.4 mm in the Y-axis and +/-5.5 mm in the Z-axis. Concordance ranged from 'mediocre' to 'satisfactory'. Proportional bias was noted between paired X- and Z-axis measures, with a constant bias component in the Z-axis. Our data suggest non-negligible differences in software-derived CBCT and KVX image-guided directional shifts using formal method comparison statistics.
Figures

References
-
- Baas J. EZ-ROSE: a computer program for equal-area circular histograms and statistical analysis of two-dimensional vectorial data. Comput Geosci. 2000;26:153–66.
-
- Balter JM, Kessler ML. Imaging and alignment for image-guided radiation therapy. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25:931–7. - PubMed
-
- Batschelet E. Circular Statistics in Biology. New York: Academic; 1981.
-
- Bel A, van Herk M, Lebesque JV. Target margins for random geometrical treatment uncertainties in conformal radiotherapy. Med Phys. 1996;23:1537–45. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
