Fine-tuning of GPCR activity by receptor-interacting proteins
- PMID: 19935667
- PMCID: PMC2825052
- DOI: 10.1038/nrm2803
Fine-tuning of GPCR activity by receptor-interacting proteins
Abstract
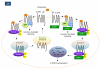
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) mediate physiological responses to various ligands, such as hormones, neurotransmitters and sensory stimuli. The signalling and trafficking properties of GPCRs are often highly malleable depending on the cellular context. Such fine-tuning of GPCR function can be attributed in many cases to receptor-interacting proteins that are differentially expressed in distinct cell types. In some cases these GPCR-interacting partners directly mediate receptor signalling, whereas in other cases they act mainly as scaffolds to modulate G protein-mediated signalling. Furthermore, GPCR-interacting proteins can have a big impact on the regulation of GPCR trafficking, localization and/or pharmacological properties.
Figures





References
-
- Bridges TM, Lindsley CW. G-protein-coupled receptors: from classical modes of modulation to allosteric mechanisms. ACS Chem Biol. 2008;3:530–41. - PubMed
-
- Reiter E, Lefkowitz RJ. GRKs and beta-arrestins: roles in receptor silencing, trafficking and signaling. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2006;17:159–65. - PubMed
-
- Moore CA, Milano SK, Benovic JL. Regulation of receptor trafficking by GRKs and arrestins. Annu Rev Physiol. 2007;69:451–82. - PubMed
-
- Premont RT, Gainetdinov RR. Physiological roles of G protein-coupled receptor kinases and arrestins. Annu Rev Physiol. 2007;69:511–34. - PubMed
-
- Hanyaloglu AC, von Zastrow M. Regulation of GPCRs by endocytic membrane trafficking and its potential implications. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2008;48:537–68. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

