The physical and genetic framework of the maize B73 genome
- PMID: 19936061
- PMCID: PMC2774505
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000715
The physical and genetic framework of the maize B73 genome
Abstract
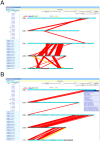
Maize is a major cereal crop and an important model system for basic biological research. Knowledge gained from maize research can also be used to genetically improve its grass relatives such as sorghum, wheat, and rice. The primary objective of the Maize Genome Sequencing Consortium (MGSC) was to generate a reference genome sequence that was integrated with both the physical and genetic maps. Using a previously published integrated genetic and physical map, combined with in-coming maize genomic sequence, new sequence-based genetic markers, and an optical map, we dynamically picked a minimum tiling path (MTP) of 16,910 bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC) and fosmid clones that were used by the MGSC to sequence the maize genome. The final MTP resulted in a significantly improved physical map that reduced the number of contigs from 721 to 435, incorporated a total of 8,315 mapped markers, and ordered and oriented the majority of FPC contigs. The new integrated physical and genetic map covered 2,120 Mb (93%) of the 2,300-Mb genome, of which 405 contigs were anchored to the genetic map, totaling 2,103.4 Mb (99.2% of the 2,120 Mb physical map). More importantly, 336 contigs, comprising 94.0% of the physical map ( approximately 1,993 Mb), were ordered and oriented. Finally we used all available physical, sequence, genetic, and optical data to generate a golden path (AGP) of chromosome-based pseudomolecules, herein referred to as the B73 Reference Genome Sequence version 1 (B73 RefGen_v1).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Moore G, Devos KM, Wang Z, Gale MD. Cereal genome evolution - grasses, line up and form a circle. Current Biology. 1995;5:737–739. - PubMed
-
- Rhoades M. Duplicate genes in maize. Am Nat. 1951;85:105–110.
-
- Wendel J, Stuber C, Edwards M, Goodman M. Duplicated chromosome segments in Zea mays L. : Further evidence from hexokinase enzymes. Theor Appl Genet. 1986;72:178–185. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

