The effect of aromatic hydrocarbon receptor on the phenotype of the Hepa 1c1c7 murine hepatoma cells in the absence of dioxin
- PMID: 19936078
- PMCID: PMC2759125
The effect of aromatic hydrocarbon receptor on the phenotype of the Hepa 1c1c7 murine hepatoma cells in the absence of dioxin
Abstract
The aromatic hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) mediates biological responses to certain exogenous ligands, such as the environmental contaminant 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD), and has also been demonstrated to modulate the cell cycle and differentiated state of several cell lines independently of exogenous ligands. In this study, we used DNA microarray analysis to elucidate the profile of genes responsive to the expression of unliganded AhR by re-introducing AhR into an AhR-deficient mouse derivative (c19) of the mouse hepatoma cell line Hepa 1c1c7. 22 gene products were up-regulated and 8 were down-regulated two-fold or more in c19 cells infected with a retroviral vector expressing mouse AhR. Surprisingly, expression of genes involved in cell proliferation or differentiation were not affected by introduction of AhR. AhR also did not restore expression of the albumin gene in c19 cells. Introduction of AhR into c12, a similar AhR-defective mouse hepatoma cell line, also did not restore albumin expression, and furthermore, did not lead to changes in cellular morphology or cell cycle parameters. These observations fail to support the notion that unliganded AhR regulates proliferation and differentiation of liver-derived cells.
Keywords: Cyp1a1; DNA microarray; albumin; aromatic hydrocarbon receptor (AhR); cell cycle; morphology.
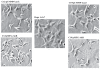
Figures


Similar articles
-
The aromatic hydrocarbon receptor modulates the Hepa 1c1c7 cell cycle and differentiated state independently of dioxin.Mol Cell Biol. 1996 May;16(5):2144-50. doi: 10.1128/MCB.16.5.2144. Mol Cell Biol. 1996. PMID: 8628281 Free PMC article.
-
Aryl hydrocarbon receptor-mediated induction of the cytosolic phospholipase A(2)alpha gene by 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin in mouse hepatoma Hepa-1c1c7 cells.J Biosci Bioeng. 2009 Oct;108(4):277-81. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiosc.2009.04.015. J Biosci Bioeng. 2009. PMID: 19716514
-
Estrogen does not inhibit 2,3,7, 8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin-mediated effects in MCF-7 and Hepa 1c1c7 cells.J Biol Chem. 1997 Nov 28;272(48):30270-4. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.48.30270. J Biol Chem. 1997. PMID: 9374512
-
Lack of antagonism of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin's (TCDDs) induction of cytochrome P4501A1 (CYP1A1) by the putative selective aryl hydrocarbon receptor modulator 6-alkyl-1,3,8-trichlorodibenzofuran (6-MCDF) in the mouse hepatoma cell line Hepa-1c1c7.Chem Biol Interact. 2004 Nov 20;150(2):161-70. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2004.09.007. Chem Biol Interact. 2004. PMID: 15535986
-
Influence of aryl hydrocarbon- (Ah) receptor and genotoxins on DNA repair gene expression and cell survival of mouse hepatoma cells.Toxicology. 2009 May 17;259(3):91-6. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2009.02.006. Epub 2009 Feb 28. Toxicology. 2009. PMID: 19428948
Cited by
-
Genome-wide RNAi high-throughput screen identifies proteins necessary for the AHR-dependent induction of CYP1A1 by 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin.Toxicol Sci. 2013 Nov;136(1):107-19. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kft191. Epub 2013 Aug 31. Toxicol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23997114 Free PMC article.
-
The aryl hydrocarbon receptor mediates raloxifene-induced apoptosis in estrogen receptor-negative hepatoma and breast cancer cells.Cell Death Dis. 2014 Jan 30;5(1):e1038. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2013.549. Cell Death Dis. 2014. PMID: 24481452 Free PMC article.
-
SIN3A, generally regarded as a transcriptional repressor, is required for induction of gene transcription by the aryl hydrocarbon receptor.J Biol Chem. 2014 Nov 28;289(48):33655-62. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.611236. Epub 2014 Oct 10. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 25305016 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of stanniocalcin 2 as a novel aryl hydrocarbon receptor target gene.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2013 Mar;344(3):579-88. doi: 10.1124/jpet.112.201111. Epub 2012 Dec 26. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2013. PMID: 23269473 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boverhof DR, Burgoon LD, Tashiro C, Chittim B, Harkema JR, Jump DB, Zacharewski TR. Temporal and dose-dependent hepatic gene expression patterns in mice provide new insights into TCDD-Mediated hepatotoxicity. Toxicol Sci. 2005;85(2):1048–63. - PubMed
-
- Boverhof DR, Burgoon LD, Tashiro C, Sharratt B, Chittim B, Harkema JR, Mendrick DL, Zacharewski TR. Comparative toxicogenomic analysis of the hepatotoxic effects of TCDD in Sprague Dawley rats and C57BL/6 mice. Toxicol Sci. 2006;94(2):398–416. - PubMed
-
- DeVito M, Birnbaum L. In: Dioxins and Health. Schecter A, editor. Plenum Press; New York: 1994. pp. 139–62.
-
- Frueh FW, Hayashibara KC, Brown PO, Whitlock JP., Jr Use of cDNA microarrays to analyze dioxin-induced changes in human liver gene expression. Toxicol Lett. 2001;122(3):189–203. - PubMed
