The 5-lipoxygenase as a common pathway for pathological brain and vascular aging
- PMID: 19936103
- PMCID: PMC2775696
- DOI: 10.1155/2009/174657
The 5-lipoxygenase as a common pathway for pathological brain and vascular aging
Abstract
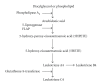
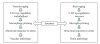
Epidemiological studies indicate age as a strong risk factor for developing cardiovascular and neurodegenerative diseases. During the aging process, changes in the expression of particular genes can influence the susceptibility to these diseases. 5-Lipoxygenase (5-LO) by oxidizing fatty acids forms leukotrienes, potent mediators of oxidative and inflammatory reactions, two key pathogenic events in both clinical settings. This enzyme is widely distributed in the cardiovascular as well as in the central nervous system, where its expression levels increase with age, suggesting that it may be involved in their diseases of aging. The central theme of this article is that during aging, 5-LO acts as biologic link between different stressors and the development of cardiovascular and neurodegenerative diseases. We hypothesize that the age-dependent upregulation of 5-LO represents a "priming" factor in the vasculature as well as in the brain, where a subsequent exposure to triggering stimuli (i.e., infections) leads to an abnormal chronic inflammatory reaction, and ultimately results in increased organ vulnerability and functional deficits.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Primary cultures of rat cerebellar granule cells as a model to study neuronal 5-lipoxygenase and FLAP gene expression.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1999;890:183-90. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1999.tb07994.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1999. PMID: 10668425
-
Aging-associated up-regulation of neuronal 5-lipoxygenase expression: putative role in neuronal vulnerability.FASEB J. 1998 Apr;12(6):439-49. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.12.6.439. FASEB J. 1998. PMID: 9535216
-
The 5-lipoxygenase enzymatic pathway in the mouse brain: young versus old.Neurobiol Aging. 2007 Sep;28(9):1457-62. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2006.06.007. Epub 2006 Aug 22. Neurobiol Aging. 2007. PMID: 16930777
-
5-lipoxygenase: cellular biology and molecular pharmacology.Curr Drug Targets Inflamm Allergy. 2002 Mar;1(1):23-44. doi: 10.2174/1568010023344959. Curr Drug Targets Inflamm Allergy. 2002. PMID: 14561204 Review.
-
Lipoxygenase Inhibitors as Cancer Chemopreventives: Discovery, Recent Developments and Future Perspectives.Curr Med Chem. 2021;28(6):1143-1175. doi: 10.2174/0929867326666191210104820. Curr Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 31820690 Review.
Cited by
-
The 5-lipoxygenase pathway: oxidative and inflammatory contributions to the Alzheimer's disease phenotype.Front Cell Neurosci. 2015 Jan 14;8:436. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2014.00436. eCollection 2014. Front Cell Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25642165 Free PMC article. Review.
-
5-Lipoxygenase DNA methylation and mRNA content in the brain and heart of young and old mice.Neural Plast. 2009;2009:209596. doi: 10.1155/2009/209596. Epub 2009 Dec 13. Neural Plast. 2009. PMID: 20052386 Free PMC article.
-
Repurposing Zileuton as a Depression Drug Using an AI and In Vitro Approach.Molecules. 2020 May 5;25(9):2155. doi: 10.3390/molecules25092155. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32380663 Free PMC article.
-
The 5-Lipoxygenase as modulator of Alzheimer's γ-secretase and therapeutic target.Brain Res Bull. 2016 Sep;126(Pt 2):207-212. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2016.03.010. Epub 2016 Mar 19. Brain Res Bull. 2016. PMID: 27005438 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of minocycline on cocaine sensitization and phosphorylation of GluR1 receptors in 5-lipoxygenase deficient mice.Neuropharmacology. 2011 Jun;60(7-8):1058-63. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2010.09.006. Epub 2010 Sep 22. Neuropharmacology. 2011. PMID: 20868701 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Najjar SS, Scuteri A, Lakatta EG. Arterial aging: is it an immutable cardiovascular risk factor? Hypertension. 2005;46(3):454–462. - PubMed
-
- Goedert M, Spillantini MG. A century of Alzheimer's disease. Science. 2006;314(5800):777–781. - PubMed
-
- Zhang X, Qi R, Xian X, et al. Spontaneous atherosclerosis in aged lipoprotein lipase-deficient mice with severe hypertriglyceridemia on a normal chow diet. Circulation Research. 2008;102(2):250–256. - PubMed
-
- Lynch MA. Age-related impairment in long-term potentiation in hippocampus: a role for the cytokine, interleukin-1β? Progress in Neurobiology. 1998;56(5):571–589. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

