The 5-lipoxygenase as a common pathway for pathological brain and vascular aging
- PMID: 19936103
- PMCID: PMC2775696
- DOI: 10.1155/2009/174657
The 5-lipoxygenase as a common pathway for pathological brain and vascular aging
Abstract
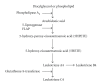
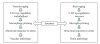
Epidemiological studies indicate age as a strong risk factor for developing cardiovascular and neurodegenerative diseases. During the aging process, changes in the expression of particular genes can influence the susceptibility to these diseases. 5-Lipoxygenase (5-LO) by oxidizing fatty acids forms leukotrienes, potent mediators of oxidative and inflammatory reactions, two key pathogenic events in both clinical settings. This enzyme is widely distributed in the cardiovascular as well as in the central nervous system, where its expression levels increase with age, suggesting that it may be involved in their diseases of aging. The central theme of this article is that during aging, 5-LO acts as biologic link between different stressors and the development of cardiovascular and neurodegenerative diseases. We hypothesize that the age-dependent upregulation of 5-LO represents a "priming" factor in the vasculature as well as in the brain, where a subsequent exposure to triggering stimuli (i.e., infections) leads to an abnormal chronic inflammatory reaction, and ultimately results in increased organ vulnerability and functional deficits.
Figures
References
-
- Najjar SS, Scuteri A, Lakatta EG. Arterial aging: is it an immutable cardiovascular risk factor? Hypertension. 2005;46(3):454–462. - PubMed
-
- Goedert M, Spillantini MG. A century of Alzheimer's disease. Science. 2006;314(5800):777–781. - PubMed
-
- Zhang X, Qi R, Xian X, et al. Spontaneous atherosclerosis in aged lipoprotein lipase-deficient mice with severe hypertriglyceridemia on a normal chow diet. Circulation Research. 2008;102(2):250–256. - PubMed
-
- Lynch MA. Age-related impairment in long-term potentiation in hippocampus: a role for the cytokine, interleukin-1β? Progress in Neurobiology. 1998;56(5):571–589. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

