Assessment of Damage to Nucleic Acids and Repair Machinery in Salmonella typhimurium Exposed to Chlorine
- PMID: 19936107
- PMCID: PMC2777018
- DOI: 10.1155/2009/201868
Assessment of Damage to Nucleic Acids and Repair Machinery in Salmonella typhimurium Exposed to Chlorine
Abstract
Water disinfection is usually evaluated using mandatory methods based on cell culturability. However, such methods do not consider the potential of cells to recover, which should also be kept as low as possible. In this paper, we hypothesized that a successful disinfection is achieved only when the applied chlorine leads to both intracellular nucleic acid damage and strong alterations of the DNA repair machinery. Monitoring the SOS system responsiveness with a umuC'-'lacZ reporter fusion, we found that the expression of this important cellular machinery was altered after the beginning of membrane permeabilization but prior to the total decline of both the cell culturability and the nucleic acid integrity as revealed by Sybr-II staining. Rapid measurement of such nucleic acid alterations by fluorochrome-based staining could be used as an alternative method for assessing the effectiveness of disinfection with chlorine.
Figures
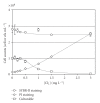
 ), cells stained by Sybr-II (
), cells stained by Sybr-II ( ), and cells stained by PI (
), and cells stained by PI ( ) versus initial applied [Cl2] (mg L−1) (22 ± 1°C) of Salmonella typhimurium.
) versus initial applied [Cl2] (mg L−1) (22 ± 1°C) of Salmonella typhimurium.
 ) or by PI (
) or by PI ( ) versus initial applied [Cl2] (mg L−1) (22 ± 1°C).
) versus initial applied [Cl2] (mg L−1) (22 ± 1°C).
References
-
- Baker RWR. Studies on the reaction between sodium hypochlorite and proteins. Biochemical Journal. 1947;41:337–342. - PubMed
-
- Hawkins CL, Pattison DI, Davies MJ. Hypochlorite-induced oxidation of amino acids, peptides and proteins. Amino Acids. 2003;25(3-4):259–274. - PubMed
-
- van den Berg JJM, Winterbourn CC, Kuypers FA. Hypochlorous acid-mediated modification of cholesterol and phospholipid: analysis of reaction products by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Journal of Lipid Research. 1993;34(11):2005–2012. - PubMed
-
- Winterbourn CC, van den Berg JJM, Roitman E, Kuypers FA. Chlorohydrin formation from unsaturated fatty acids reacted with hypochlorous acid. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics. 1992;296(2):547–555. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

