Messenger RNA Turnover Processes in Escherichia coli, Bacillus subtilis, and Emerging Studies in Staphylococcus aureus
- PMID: 19936110
- PMCID: PMC2777011
- DOI: 10.1155/2009/525491
Messenger RNA Turnover Processes in Escherichia coli, Bacillus subtilis, and Emerging Studies in Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
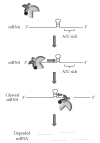
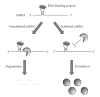
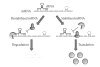
The regulation of mRNA turnover is a recently appreciated phenomenon by which bacteria modulate gene expression. This review outlines the mechanisms by which three major classes of bacterial trans-acting factors, ribonucleases (RNases), RNA binding proteins, and small noncoding RNAs (sRNA), regulate the transcript stability and protein production of target genes. Because the mechanisms of RNA decay and maturation are best characterized in Escherichia coli, the majority of this review will focus on how these factors modulate mRNA stability in this organism. However, we also address the effects of RNases, RNA binding proteins, sRNAs on mRNA turnover, and gene expression in Bacillus subtilis, which has served as a model for studying RNA processing in gram-positive organisms. We conclude by discussing emerging studies on the role modulating mRNA stability has on gene expression in the important human pathogen Staphylococcus aureus.
Figures
References
-
- Takayama K, Kjelleberg S. The role of RNA stability during bacterial stress responses and starvation. Environmental Microbiology. 2000;2(4):355–365. - PubMed
-
- Jiang W, Hou Y, Inouye M. CspA, the major cold-shock protein of Escherichia coli, is an RNA chaperone. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1997;272(1):196–202. - PubMed
-
- Fang L, Jiang W, Bae W, Inouye M. Promoter-independent cold-shock induction of cspA and its derepression at 37°C by mRNA stabilization. Molecular Microbiology. 1997;23(2):355–364. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

