Progression of renal dysfunction in patients with cardiovascular disease
- PMID: 19936196
- PMCID: PMC2780821
- DOI: 10.2174/157340308785160543
Progression of renal dysfunction in patients with cardiovascular disease
Abstract
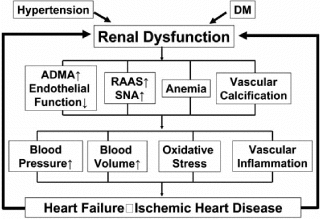
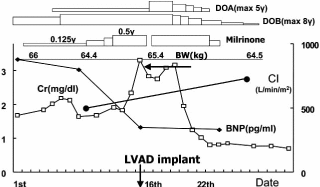
It has been established that patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) suffer from frequent cardiovascular events. On the other hand, recent studies suggest that renal damage tends to worsen in patients with cardiovascular diseases (CVD). Although the mechanisms for the cardiorenal association are unclear, the presence of arteriosclerotic risk factors common to both CVD and CKD is important. In arteriosclerosis, vascular derangement progresses not only in the heart but also in the kidney. In addition, heart failure, cardiac catheterization and hesitation of medical treatments due to renal dysfunction may explain the progression of renal damage. Therefore, the goal of treatments is a total control of arteriosclerotic risk factors. Medication should be selected among agents with protective effects on both heart and kidney. It is important to always consider the presence of CKD for the treatment of the cardiovascular disease and strictly control the risk factors.
Keywords: ARB; CKD; aldosterone; angiotensin II; hypertension..
Figures

References
-
- Go AS, Chertow GM, Fan D, McCulloch CE, Hsu CY. Chronic kidney disease and the risks of death, cardiovascular events, and hospitalization. N Engl J Med. 2004;351:1296–305. - PubMed
-
- Schrier RW. Role of diminished renal function in cardiovascular mortality: marker or pathogenetic factor? J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006;47:1–8. - PubMed
-
- McCullough PA, Jurkovitz CT, Pergola PE, et al. Independent components of chronic kidney disease as a cardiovascular risk state: results from the Kidney Early Evaluation Program (KEEP) Arch Intern Med. 2007;167:1122–9. - PubMed
-
- Levin A, Djurdjev O, Barrett B, et al. Cardiovascular disease in patients with chronic kidney disease: getting to the heart of the matter. Am J Kidney Dis. 2001;38:1398–407. - PubMed
-
- O'Hare AM, Rodriguez RA, Bacchetti P. Low ankle-brachial index associated with rise in creatinine level over time: results from the atherosclerosis risk in communities study. Arch Intern Med. 2005;165:1481–5. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

