Incidence, seasonality and mortality associated with influenza pneumonia in Thailand: 2005-2008
- PMID: 19936224
- PMCID: PMC2777392
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0007776
Incidence, seasonality and mortality associated with influenza pneumonia in Thailand: 2005-2008
Abstract
Background: Data on the incidence, seasonality and mortality associated with influenza in subtropical low and middle income countries are limited. Prospective data from multiple years are needed to develop vaccine policy and treatment guidelines, and improve pandemic preparedness.
Methods: During January 2005 through December 2008, we used an active, population-based surveillance system to prospectively identify hospitalized pneumonia cases with influenza confirmed by reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction or cell culture in 20 hospitals in two provinces in Thailand. Age-specific incidence was calculated and extrapolated to estimate national annual influenza pneumonia hospital admissions and in-hospital deaths.
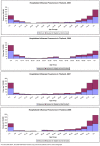
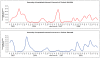
Results: Influenza was identified in 1,346 (10.4%) of pneumonia patients of all ages, and 10 influenza pneumonia patients died while in the hospital. 702 (52%) influenza pneumonia patients were less than 15 years of age. The average annual incidence of influenza pneumonia was greatest in children less than 5 years of age (236 per 100,000) and in those age 75 or older (375 per 100,000). During 2005, 2006 and 2008 influenza A virus detection among pneumonia cases peaked during June through October. In 2007 a sharp increase was observed during the months of January through April. Influenza B virus infections did not demonstrate a consistent seasonal pattern. Influenza pneumonia incidence was high in 2005, a year when influenza A(H3N2) subtype virus strains predominated, low in 2006 when A(H1N1) viruses were more common, moderate in 2007 when H3N2 and influenza B co-predominated, and high again in 2008 when influenza B viruses were most common. During 2005-2008, influenza pneumonia resulted in an estimated annual average 36,413 hospital admissions and 322 in-hospital pneumonia deaths in Thailand.
Conclusion: Influenza virus infection is an important cause of hospitalized pneumonia in Thailand. Young children and the elderly are most affected and in-hospital deaths are more common than previously appreciated. Influenza occurs year-round and tends to follow a bimodal seasonal pattern with substantial variability. The disease burden varies significantly from year to year. Our findings support a recent Thailand Ministry of Public Health (MOPH) decision to extend annual influenza vaccination to older adults and suggest that children should also be targeted for routine vaccination.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Coffin SE, Zaoutis TE, Rosenquist AB, Heydon K, Herrera G, et al. Incidence, complications, and risk factors for prolonged stay in children hospitalized with community-acquired influenza. Pediatrics. 2007;119:740–748. - PubMed
-
- Poehling KA, Edwards KM, Weinberg GA, Szilagyi P, Staat MA, et al. The underrecognized burden of influenza in young children. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:31–40. - PubMed
-
- Gravenstein S, Davidson HE. Current strategies for management of influenza in the elderly population. Clin Infect Dis. 2002;35:729–737. - PubMed
-
- Molinari NA, Ortega-Sanchez IR, Messonnier ML, Thompson WW, Wortley PM, et al. The annual impact of seasonal influenza in the US: measuring disease burden and costs. Vaccine. 2007;25:5086–5096. - PubMed
-
- Heikkinen T, Silvennoinen H, Peltola V, Ziegler T, Vainionpaa R, et al. Burden of influenza in children in the community. J Infect Dis. 2004;190:1369–1373. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

