Diversity of Pol IV function is defined by mutations at the maize rmr7 locus
- PMID: 19936246
- PMCID: PMC2775721
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000706
Diversity of Pol IV function is defined by mutations at the maize rmr7 locus
Abstract
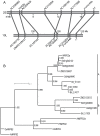
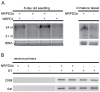
Mutations affecting the heritable maintenance of epigenetic states in maize identify multiple small RNA biogenesis factors including NRPD1, the largest subunit of the presumed maize Pol IV holoenzyme. Here we show that mutations defining the required to maintain repression7 locus identify a second RNA polymerase subunit related to Arabidopsis NRPD2a, the sole second largest subunit shared between Arabidopsis Pol IV and Pol V. A phylogenetic analysis shows that, in contrast to representative eudicots, grasses have retained duplicate loci capable of producing functional NRPD2-like proteins, which is indicative of increased RNA polymerase diversity in grasses relative to eudicots. Together with comparisons of rmr7 mutant plant phenotypes and their effects on the maintenance of epigenetic states with parallel analyses of NRPD1 defects, our results imply that maize utilizes multiple functional NRPD2-like proteins. Despite the observation that RMR7/NRPD2, like NRPD1, is required for the accumulation of most siRNAs, our data indicate that different Pol IV isoforms play distinct roles in the maintenance of meiotically-heritable epigenetic information in the grasses.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
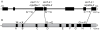
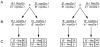
References
-
- Luo J, Hall BD. A multistep process gave rise to RNA polymerase IV of land plants. J Mol Evol. 2007;64 (1):101–112. - PubMed
-
- Arabidopsis Genome Initiative. Analysis of the genome sequence of the flowering plant Arabidopsis thaliana. Nature. 2000;408:796–815. - PubMed
-
- Herr AJ, Jensen MB, Dalmay T, Baulcombe DC. RNA polymerase IV directs silencing of endogenous DNA. Science. 2005;308:118–120. - PubMed
-
- Kanno T, Huettel B, Mette MF, Aufsatz W, Jaligot E, et al. Atypical RNA polymerase subunits required for RNA-directed DNA methylation. Nat Genet. 2005;37:761–765. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

