The zebrafish lens proteome during development and aging
- PMID: 19936306
- PMCID: PMC2779061
The zebrafish lens proteome during development and aging
Abstract
Purpose: Changes in lens protein expression during zebrafish development results in a smooth gradient of refractive index necessary for excellent optical function. Age-related changes in crystallin expression have been well documented in mammals but are poorly understood in the zebrafish.
Methods: In the zebrafish lens, a systematic analysis of protein content with age was performed using size exclusion chromatography (SEC) combined with linear trap quadrupole Fourier transform tandem mass spectrometry (LTQ-FT LC-MS/MS; rank-order shotgun) proteomics in lenses of larval, juvenile, and adult zebrafish.
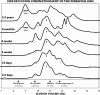
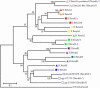
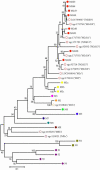
Results: alpha-Crystallins, previously shown to have low abundance in the zebrafish lens, were found to increase dramatically with maturation and aging. SEC determined that beta-crystallin was predominant at 4.5 days. With age, the alpha- and gamma-crystallins increased, and a high molecular weight fraction appeared between six weeks and six months to become the dominant component by 2.5 years. Similarly, shotgun proteomics determined that beta-crystallins were the predominant proteins in the young lens. With age, the proportion of alpha- and gamma-crystallins increased dramatically. After crystallins, calpain 3, membrane, and cytoskeletal proteins were most abundant. Five new beta-crystallins and 13 new gamma-crystallins were identified.
Conclusions: As expected, SEC and proteomics demonstrated changing levels of protein expression with age, especially among the crystallins. The results also confirmed the existence of novel crystallins in the zebrafish genome.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Changes in zebrafish (Danio rerio) lens crystallin content during development.Mol Vis. 2013;19:408-17. Epub 2013 Feb 18. Mol Vis. 2013. PMID: 23441112 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative proteomics analysis of degenerative eye lenses of nocturnal rice eel and catfish as compared to diurnal zebrafish.Mol Vis. 2013;19:623-37. Epub 2013 Mar 20. Mol Vis. 2013. PMID: 23559856 Free PMC article.
-
A proteome map of the zebrafish (Danio rerio) lens reveals similarities between zebrafish and mammalian crystallin expression.Mol Vis. 2008 Apr 25;14:806-14. Mol Vis. 2008. PMID: 18449354 Free PMC article.
-
Spatiotemporal changes in the human lens proteome: Critical insights into long-lived proteins.Prog Retin Eye Res. 2020 May;76:100802. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2019.100802. Epub 2019 Nov 6. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2020. PMID: 31704338 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Proteome of Cataract Markers: Focus on Crystallins.Adv Clin Chem. 2018;86:179-210. doi: 10.1016/bs.acc.2018.05.005. Epub 2018 Jul 13. Adv Clin Chem. 2018. PMID: 30144840 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparative proteomic analysis identifies age-dependent increases in the abundance of specific proteins after deletion of the small heat shock proteins αA- and αB-crystallin.Biochemistry. 2013 Apr 30;52(17):2933-48. doi: 10.1021/bi400180d. Epub 2013 Apr 16. Biochemistry. 2013. PMID: 23590631 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of α-crystallin protein loss on zebrafish lens development.Exp Eye Res. 2023 Feb;227:109358. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2022.109358. Epub 2022 Dec 23. Exp Eye Res. 2023. PMID: 36572168 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in zebrafish (Danio rerio) lens crystallin content during development.Mol Vis. 2013;19:408-17. Epub 2013 Feb 18. Mol Vis. 2013. PMID: 23441112 Free PMC article.
-
Some Aspects of Development and Histological Structure of the Visual System of Nothobranchius Guentheri.Animals (Basel). 2021 Sep 21;11(9):2755. doi: 10.3390/ani11092755. Animals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34573720 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo analysis of aquaporin 0 function in zebrafish: permeability regulation is required for lens transparency.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2013 Jul 30;54(7):5136-43. doi: 10.1167/iovs.13-12337. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2013. PMID: 23800763 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Benedek GB. Theory of transparency of the eye. Appl Opt. 1971;10:459–73. - PubMed
-
- Delaye M, Tardieu A. Short-range order of crystallin proteins accounts for eye lens transparency. Nature. 1983;302:415–7. - PubMed
-
- Clark JI. Order and disorder in the transparent media of the eye. Exp Eye Res. 2004;78:427–32. - PubMed
-
- Prescott AR, Sandilands A, Hutcheson AM, Carter JM, Quinlan RA. The intermediate filament cytoskeleton of the lens: an ever changing network through development and differentiation. A minireview. Ophthalmic Res. 1996;28(Suppl 1):58–61. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
